19 Feb 2016
Biomass Energy exploration at Northeast Biomass Heating Expo in Burlington, Vermont March 30 – April 1

Northeast Biomass Heating Expo to be held in Burlington, Vermont March 30 – April 1
The 8th annual Northeast Biomass Heating Expo will be held March 30 – April 1 at the Sheraton Hotel and Conference Center in Burlington, Vermont. The Expo has become one of the fastest growing biomass thermal energy conferences in the United States, with almost 2,000 attendees expected this year. There will also be over 400 businesses, agencies and organizations present to contribute to the event’s comprehensive knowledge base of biomass thermal heating.
Biomass heating is a widely available source of renewable energy, which can help meet the heating needs of homes and businesses while displacing fossil fuels. The types of biomass most commonly used for energy include waste wood form the timber and wood products industries, as well as agriculture residues. These fuels can either be directly combusted, or they can undergo a variety of refining processes such as chipping or pelletization for use in a variety of home and industry heating applications.
Speakers, panel discussions, presentations, educational sessions and additional opportunities for tours and workshops will be available at this year’s expo. It is an excellent opportunity for networking with organizations, government, and across the broader biomass industry.
The Northeast Biomass Heating Expo is currently seeking co-hosts to help promote and be promoted at the event. Non-profit organizations, trade associations, community groups, and government agencies are all invited to become an event co-host. Co-host organization’s name and logo will be prominently displayed on conference communication outlets, and receive a free display tabletop at the event to share information with attendees. They will also be recognized during the opening and closing events and receive a special extension of the ‘Early Bird’ rate by one month.
Learn more about the Northeast Biomass Heating Expo at www.nebiomassheat.com.
02 Nov 2015
Vermont Bioenergy Initiative proves biofuel potential for state and concludes ten year project
By: Ellen Kahler

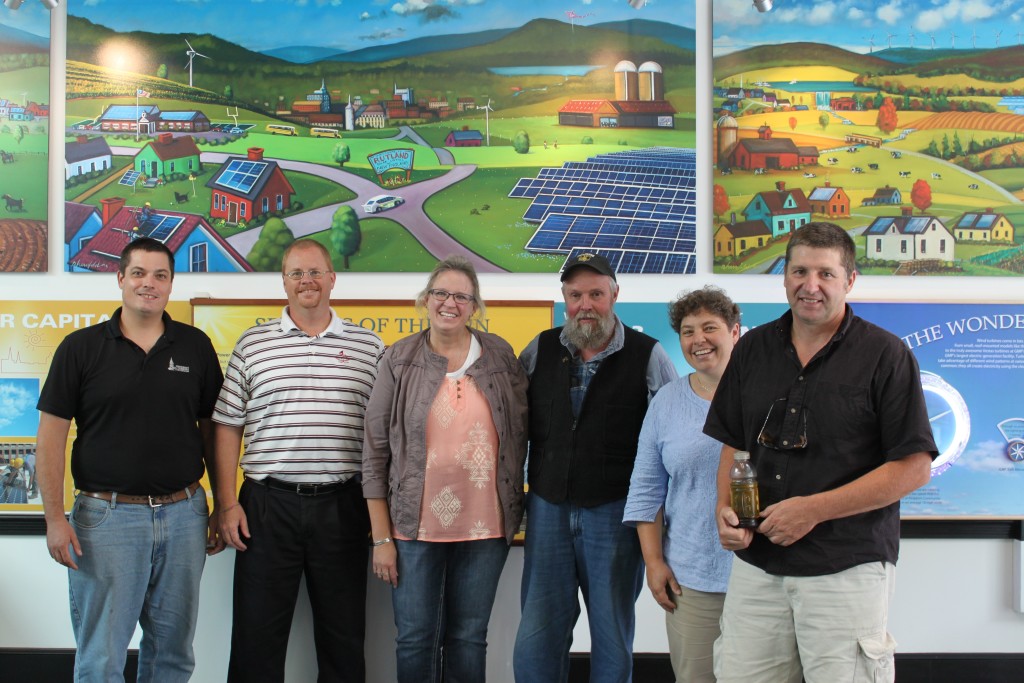
VT Bioenergy Team – L to R (Chris Callahan – UVM Extension, Kirk Shields — Green Mountain Power, Christy Sterner – US DOE, Larry Scott – Ekolott Farm, Ellen Kahler – VSJF, John Williamson – Stateline Biofuels) at Green Mountain Power’s Energy Innovation Center in Rutland
Vermont can produce more of its own biofuel energy and the environmental and potential economic benefits of local bioenergy have been proven by the Vermont Bioenergy Initiative – a program of the Vermont Sustainable Jobs Fund. Since 2005, the Vermont Bioenergy Initiative has invested more than $2.5 million in innovative bioenergy research, projects, and people so Vermont can locally produce more of the state’s energy needs – from a variety of agricultural and algal feedstocks.
US Senator Patrick Leahy made the investment at this scale possible through Congressionally Directed Awards from the US Department of Energy (US DOE). The funding concludes in early 2016, at which point a complete impact report will be released by the Vermont Sustainable Jobs Fund, who has served as the intermediary between the US DOE and 52 individual Vermont bioenergy projects over the past ten years.
Research, development, and early stage demonstration projects have included:
- Investing in 2 on-farm methane digesters;
- Building farm-scale infrastructure to turn oilseed crops such as sunflowers into biodiesel to run farm tractors;
- Growing switchgrass and densifying it into “pucks” that are burned in a high efficiency commercial boiler instead of propane;
- Identifying the most lipid producing strains of native Vermont algae which can feed off the excess nutrients from methane digesters and can eventually be harvested to make biodiesel or jet fuel;
- Developing two “Biomass to Biofuels” college level courses which run repeatedly at UVM and VT Tech to inspire and train the next generation of bioenergy experts and technicians;
- Exploring the logistics of bulk wood pellet delivery systems to Vermonters’ homes;
- Organizing a number of learning opportunities and conferences for oilseed, grass and algae researchers, farmers and entrepreneurs to attend;
- Providing agronomic and engineering support to oilseed and grass farmers;
- Educating the general public about why the local production for local use of energy crops from Vermont farms and forests makes good economic and ecological sense.

VT Bioenergy Team 2 – L to R (Roger Rainville – Borderview Farm, Christy Sterner – US DOE, Heather Darby – UVM Extension, Natasha Rainville – Borderview Farm) at Borderview Farm, Alburgh VT
The Vermont Bioenergy Initiative is a unique effort and one that is gaining resonance in other parts of rural America. The initiative’s resource website, www.VermontBioenergy.com is utilized by biofuel producers, educators, and technical service providers from across the country.
The work conducted over the past ten years by the Vermont Bioenergy Initiative to conduct research, provide technical assistance, and develop infrastructure in emerging areas of bioenergy will continue with the initiative’s partners at UVM Extension and the Vermont Agency of Agriculture, Food & Markets. As Vermont moves forward – being innovative and increasingly focused on generating renewable energy from the land and forests – the research and infrastructure the Vermont Bioenergy Initiative has invested in over the past ten years will endure and spawn the next wave of bioenergy development in the state.
Ellen Kahler is executive director of the Vermont Sustainable Jobs Fund (VSJF), a non-profit organization created by the State of Vermont to help develop Vermont’s sustainable agriculture, renewable energy, and forest product businesses. Since 2005, the Vermont Bioenergy Initiative has been a VSJF program that connects diversified agriculture and local renewable energy production for on-farm and community use by supporting research, technical assistance, and infrastructure development in emerging areas of bioenergy including biodiesel production and distribution for heating and transportation, oil crops for on-farm biodiesel and feed, grass for heating, and algae production for biofuels and wastewater management. Learn more at www.VermontBioenergy.com.
 Algae for biofuel has been a long time component of the local biofuel production for local use model pioneered by the Vermont Bioenergy Initiative. At the forefront of these efforts has been Anju Dahyia, a VBI grantee, lead biofuels instructor at the University of Vermont, and president of General Systems Research (GSR) Solutions. When the Vermont Fuel Dealers Association received a USDA Rural Business Enterprise Grant to utilize waste materials from Vermont farms to produce sustainable distillate fuel, Anju and GRS Solutions were already in a prime positon to conduct the necessary research.
Algae for biofuel has been a long time component of the local biofuel production for local use model pioneered by the Vermont Bioenergy Initiative. At the forefront of these efforts has been Anju Dahyia, a VBI grantee, lead biofuels instructor at the University of Vermont, and president of General Systems Research (GSR) Solutions. When the Vermont Fuel Dealers Association received a USDA Rural Business Enterprise Grant to utilize waste materials from Vermont farms to produce sustainable distillate fuel, Anju and GRS Solutions were already in a prime positon to conduct the necessary research.
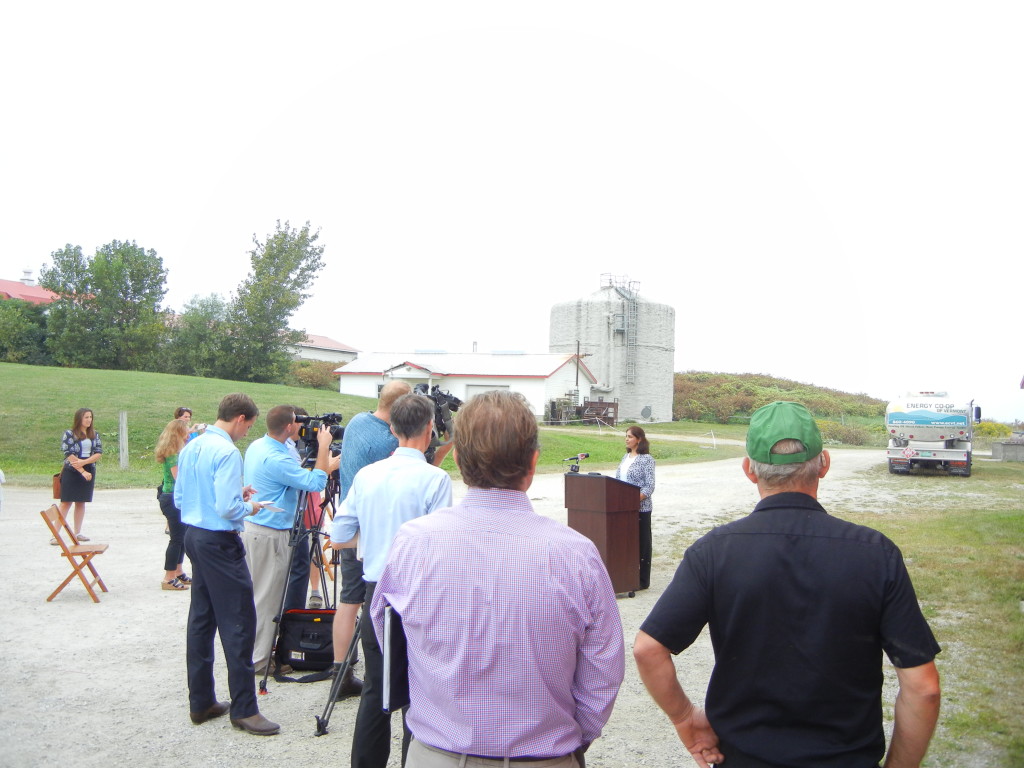
GSR is developing a method of producing algae biofuel to replace traditional fossil fuels in motor vehicles, heavy farm equipment, and even airplanes at Charlotte’s Nordic Dairy Farm as a second tier to the already operational anaerobic digesters contributing to Vermont’s distributed energy generation grid. The process to produce algal biofuel has the potential to prevent nutrients such as phosphorus and nitrogen from making their way into local lakes and waterways. Nordic Dairy Farm’s owner, Clark Hinsdale, explained at a recent press event on his farm: “the best way to capture excess nutrients on farms is to never let them get beyond the boundaries of the farmstead.”
The current anaerobic digestion system “Cow Power,” utilized by Green Mountain Power, functions by using the methane byproduct harvested from constantly produced cow manure to make electricity that then is sold to Green Mountain Power customers. The research done by GSR focuses on another byproduct of digestion – the nutrient dense liquid waste, previously left unused for power purposes.
The oleaginous algae strains that Anju Dahyia has been working with since 2008 thrive on this dense waste and after the algae has consumed the available nutrients, the creation of the distillate fuel can begin. The result makes the process a closed loop system, and means that dairy farmers like Nordic Dairy (whose cows produce up to a ton of manure a day) would be able to sell algae derived biofuel to local fuel dealers and create granular organic fertilizer. According to Dahyia, Hinsdale’s 300 cows alone have the potential to produce anywhere between 20,000 to 30,000 gallons of biofuel each year.
The cost of production is estimated at $20 dollars per gallon, but Dahyia thinks that with increased scale will come a decreased price. At the recent press conference at the Nordic Dairy Farm site early in September, Mary Powell of Green Mountain Power outlined how the company is working with GSR Solutions to help increase scale and add more small refineries that mimic this operation. She went on to note the resiliency a community-sized digester refinery can add to a microgrid.
Speaking to ABC local 22 News, Matt Cota, Director of the Vermont Fuel Dealers Association added, “We know that bio-heat, renewable blended fuel, combined with heating oil works in customers tanks and burners, so if we can source that locally, it would be a great thing for Vermont’s economy, for Vermont famers, Vermont fuel dealers and consumers all across Vermont.”
Richard Altman of the non-profit Commercial Aviation Fuels Initiative was also in attendance and trumpeted that “community-scale digester-refineries in the region might be feasible by 2020,” noting that this project is just a start.
Also on the horizon, GRS Solutions is already working to go further with this technology by incorporating food waste into this digester system. While this system may be in its early stages, one thing is for sure, Vermont energy stakeholders are lining up to show their support and contribute to this more than viable option for local energy production.
For more watch the local WCAX coverage of the September 3rd press conference and to learn more about Algae Bioenergy in Vermont see our other post Algae Biofuel – Vermont’s Search for Viable and Cost-Effective Methods
19 Oct 2015
Field to Flue Open House at Meach Cove Farms

Vermont-grown grasses are being used to heat the Biomass Building – a 4,200 square foot commercial building at Meach Cove Farms in Shelburne. Local residents, community leaders, and renewable energy enthusiasts are invited to visit Meach Cove Farms Friday, October 23 – Saturday, October 24 for an Open House to learn how grass pellets are generating heat in a biomass boiler – an emerging source of bioenergy in Vermont.
Meach Cove Farms is a 1,000-acre certified organic farm primarily growing soy beans, wheat, rye, and corn as well as wine grapes, woodlands, and switchgrass trial plots for use in grass energy production. The Open House will offer a complete demonstration of the Grass Pellet Heating Equipment Combustion Optimization project – the first project in New England to showcase grass test plots, densification equipment, and an EvoWorld biomass boiler that burns the grass.
Meach Cove Farms began collaborating with Dr. Sidney Bosworth of the University of Vermont College of Agriculture and Life Sciences and the Vermont Bioenergy Initiative in 2009 to assess the potential of different species of grass as solid biofuel for heating applications.
In September 2011 Meach Cove Farms was awarded an USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service Conservation Innovation Grant to research the feasibility of Vermont grown grass pellets and heating equipment potential as an emerging renewable energy source in Vermont. The biomass boiler being featured at the Open House was funded through a Conservation Innovation Grant (CIG) administered by the Natural Resources Conservation Services.
IF YOU GO:
Meach Cove Farms is located at 310 Beach Road in Shelburne (off Bostwick Road, 1.6 miles west of Rte 7). The Open House runs from 9 am – 12 noon both Friday and Saturday, October 23-24. There is no cost and both days are open to the public. More info at www.meachcovefarms.org, 802-985-9218.
 Efficiency Vermont, Renewable Energy Resource Center, Renewable Energy Vermont and Clean Energy Development Fund combine efforts to bring up to $5,500 in rebates to Vermonters who heat local
Efficiency Vermont, Renewable Energy Resource Center, Renewable Energy Vermont and Clean Energy Development Fund combine efforts to bring up to $5,500 in rebates to Vermonters who heat local
Through a generous opportunity, Vermonters now have a short-time frame before the new year to capitalize on a fantastic incentive offering that helps them save money, while supporting Vermont jobs and sustainable forests, while making sure they stay warm this winter.
Vermonters can get up to $5,500 to help switch from fossil fuel to local wood heating. Cash incentives are available from the Clean Energy Development Fund and Efficiency Vermont. Renewable Energy Vermont and the Renewable Energy Resource Center have partnered to help promote the incentives.
“We’ve been very happy with our decision to switch to a wood pellet boiler. Not only do we save money every year on our fuel bill, but we also love the fact that we’re helping to keep forests intact and logging jobs going,” says Mark Bushnell of Middlesex.
Vermonters who make the switch to wood pellet fuel typically save $1,500 annually when compared to oil and propane fuel heating options. And for those who are used to whole-home heating through their traditional boiler, the wood pellet boiler keeps it simple and complete. Advanced wood pellet boilers are fully automatic, so there’s no work for the home or business owner.
“I heated my home for years with a standard wood stove, but I’m happier with my wood pellet boiler. The new boiler is much more efficient and better for the environment because it is cleaner burning. And it feels great to be off fossil fuels,” says Susan Clark of Middlesex.
Wood pellet boilers, though not well known in the United States, are the primary way of heating in some parts of the world, including Upper Austria where more than 40,000 homes and businesses heat with wood from their background in an easy, seamless way. In fact, the State of Vermont and Upper Austria are involved in a Sister Statehood Agreement to help learning across both sides of the Atlantic to increase the uptake of this sustainable, local heating option.
“For many years, Vermont has been a national leader in the use of modern wood heating systems in large buildings like schools, office buildings, and apartment buildings. With pellets now available in bulk using specialized delivery trucks that conveniently blow pellets into a fuel bin and heating systems that are fully-automated, many homeowners and small businesses are also making the switch from oil and propane,” said Adam Sherman of the Biomass Energy Resource Center.
For more information, please go to www.advancedwoodheat.com
Media Contacts:
Renewable Energy Vermont, Ansley Bloomer, ansley@revermont.org (802) 595-0723
Biomass Energy Resource Center, Alayna Howard, ahoward@veic.org (802) 540-7656
Renewable Energy Resource Center, Alayna Howard, ahoward@veic.org (802) 540-7656
Efficiency Vermont, Alayna Howard, ahoward@veic.org (802) 540-7656
Clean Energy Development Fund, Andrew Perchlik, andrew.perchlik@state.vt.us (802) 828-4017
17 Aug 2015
The Third Annual National Bioenergy Day
The T hird Annual National Bioenergy Day (NBD), which will take place Wednesday, October 21st, is a day that is marked with events from across the country that celebrates energy independence, local jobs, and many other benefits of local bioenergy. Led by Biomass Power Association in partnership with U.S. Forest Service, National Bioenergy Day is an opportunity for Vermonters to showcase our research, progress, and impacts in producing local bioenergy for local use.
hird Annual National Bioenergy Day (NBD), which will take place Wednesday, October 21st, is a day that is marked with events from across the country that celebrates energy independence, local jobs, and many other benefits of local bioenergy. Led by Biomass Power Association in partnership with U.S. Forest Service, National Bioenergy Day is an opportunity for Vermonters to showcase our research, progress, and impacts in producing local bioenergy for local use.
How To Get Involved:
- Organize an event on or near October 21ndthat showcases bioenergy as a clean, efficient, and resourceful way to produce energy. Emphasizes bioenergy’s role in improving environmental health; and facilitates collaboration along the supply chain.
- Partner with someone who works in the bioenergy supply chain to create an event. Use the Vermont Energy Atlas to find partners in your area.
- Piggyback on an existing event and call it a NBD event.
- Share and talk about NBD in your social media and press efforts while promoting impacts in your community.
The Vermont Bioenergy Initiative, for example, will spend the day re-capping and previewing events and research on our Twitter handle @VTBioenergy that took place throughout the summer and that are planned for the fall. We’ll be recapping and sharing exciting things like the exciting learning opportunities at the University of Vermont, Full Sun Company’s Biodiesel and Meal production, and much more!
For more information, you can visit also visit bioenergyday.com and follow @USAbiomass on twitter!
Click Here for National Bioenergy Day Participation Guide!
27 Jul 2015
Summit on Creating Prosperity and Opportunity Confronting Climate Change – Looking Back and Looking Forward
 The Summit on Creating Prosperity and Opportunity Confronting Climate Change brought together over 400 innovative business, non‐profit, and community leaders, elected officials, public policy advocates, students, and interested residents to begin to frame policy and investment strategies to advance the development of the Vermont Climate Economy. Summit participants developed a list of key practical actions to serve as a launching point for the Vermont Climate Change Economy Council (VCCEC), a group charged with a one year mission to develop a structured plan with practical actions to reduce carbon emissions and stimulate green economic development in Vermont. The Council will build a set of public/private strategies designed to promote economic opportunity, innovative business development, investment, and job creation in Vermont.
The Summit on Creating Prosperity and Opportunity Confronting Climate Change brought together over 400 innovative business, non‐profit, and community leaders, elected officials, public policy advocates, students, and interested residents to begin to frame policy and investment strategies to advance the development of the Vermont Climate Economy. Summit participants developed a list of key practical actions to serve as a launching point for the Vermont Climate Change Economy Council (VCCEC), a group charged with a one year mission to develop a structured plan with practical actions to reduce carbon emissions and stimulate green economic development in Vermont. The Council will build a set of public/private strategies designed to promote economic opportunity, innovative business development, investment, and job creation in Vermont.
Over the course of 2015, VCCEC will evaluate findings, key ideas and suggested action steps derived from the Summit, lead regional public forums, evaluate and summarize research findings, interview key stakeholder groups, and consider model economic development strategies from other state and countries. During 2015, the group will develop a strategic platform of recommendations for action, and report to the Vermont legislature, the Governor of Vermont and the public in January 2016. The Vermont Council on Rural Development (VCRD) will provide support to their work and then help promote the platform of action that comes from its deliberants. Goals of the Vermont Climate Change Economy Council are to:
- Identify opportunities created by climate change to strengthen Vermont’s economy through strategies advancing key business clusters and economic sectors.
- Build an increased sense of unity in Vermont around policies to confront and mitigate the impact of climate change and to advance economic opportunities and solutions that respond to climate change.
- Build a public information campaign to celebrate innovation and Vermont’s green business leadership; internally and externally marketing to build the Vermont brand as an economic/environmental problem solver.
- Expand Vermont’s economic brand around climate change solutions to retain and attract youth and creative entrepreneurs to locate throughout the state.
Vermont businesses and nonprofits are addressing climate change – both its challenges and opportunities. Their creative solutions are a growing part of our state’s economy. What are your experiences? Do you have ideas about how Vermont can grow jobs and nurture innovative business development in sectors ranging from clean energy, to recycling, transportation systems, and thermal efficiency?
Jo![Regional_Forum_Flyer5_15_statewide[1]](https://vermontbioenergy.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/Regional_Forum_Flyer5_15_statewide1-150x150.jpg) in the Vermont Council on Rural Development and local business leaders at a forum on “What’s Next for Vermont’s Climate Change Economy?” Forums will take place at 7:00pm at the Paramount in Rutland (Aug 26), the Latchis Hotel in Brattleboro (Oct 6), and City Hall in Burlington (Oct 29). Come to the forum(s) most convenient for you.
in the Vermont Council on Rural Development and local business leaders at a forum on “What’s Next for Vermont’s Climate Change Economy?” Forums will take place at 7:00pm at the Paramount in Rutland (Aug 26), the Latchis Hotel in Brattleboro (Oct 6), and City Hall in Burlington (Oct 29). Come to the forum(s) most convenient for you.
These forums are the next step for public input to the Vermont Climate Change Economy Council, a group working to develop a practical plan to reduce carbon emissions and stimulate economic development in Vermont. To learn more about the forums and the Council visit VCRD’s website at vtrural.org, download the event flyer (pdf).
For more information about the results of the summit, Click HERE to read the report and follow the hashtag #VTClimateEconomy and Vermont Council on Rural Development on Twitter at @VTRuralDev for more updates!
13 Jul 2015
Making Biofuel
 Making biofuel, it sounds like a complicated process taking place in a laboratory somewhere, but in reality it’s quite simple and happening in small, rural Vermont farms. Vermont farmers like John Williamson of State Line Farm and others are electing to create their own fuel and meal. These farmers are enjoying the benefits of the distance to source resiliency and cost reliability that comes with the local production for local use biofuel model they have adopted.
Making biofuel, it sounds like a complicated process taking place in a laboratory somewhere, but in reality it’s quite simple and happening in small, rural Vermont farms. Vermont farmers like John Williamson of State Line Farm and others are electing to create their own fuel and meal. These farmers are enjoying the benefits of the distance to source resiliency and cost reliability that comes with the local production for local use biofuel model they have adopted.
As John Williamson, a Vermont Bioenergy grant recipient says, “100 years ago everyone produced their own fuel; we are just doing that now in a different way.” This is a novel way to look at what he is doing on his North Bennington farm. Vermont farmers in the past would plan to allocate their acreage to feed their livestock, some of which aided in energy-intensive farm activities like plowing, planting, and the eventual harvesting of their field. With the local production for local use model, John is now thinking about how to feed his tractor so he can do the same activities. So what is the feed of choice for John’s John Deer tractor? Sunflowers!
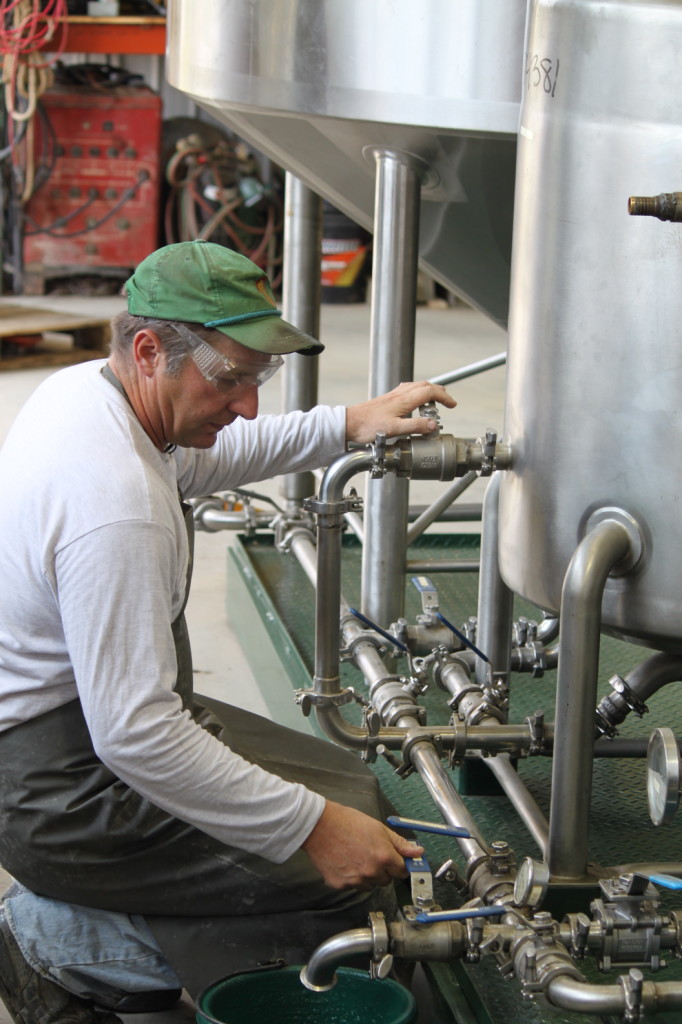
John loads dry and clean sunflower seeds into hoppers on a TabyPressen Oilpress, where screw augers push the seed through a narrow dye. Extracted oil oozes from the side of the barrel and is collected in settling tanks while pelletized meal is pushed through the dye at the front and is stored in one-ton agricultural sacks. The first of the two byproducts, the seed meal, can fuel pellet stoves, serve as fertilizer for crops, or find its way to local Vermont farms to supplement animal nutrition as livestock feed. The second byproduct, the fuel, could at this point be used as culinary oil for cooking, but instead will experience further refinement and become biofuel.
The processing of the oil takes place in Johns self-designed Biobarn. In the below video, John Williamson and Chris Callahan of University of Vermont Extension show us how they can grow oil crops, make biodiesel, feed animals, and save money!
29 Jun 2015
Soybeans for On-farm Biodiesel Production
Mark Mordasky, owner of Rainbow Valley Farm in Orwell, Vermont has been growing soybeans as a cash crop and for on-farm biodiesel and animal feed since 2008. When fuel prices began to climb, Mark took initiative and started searching for an innovative and more cost efficient way to meet his farm’s energy demands. The Vermont Sustainable Jobs Fund was able to help Mark take his first steps towards sustainable biofuel production. Mark is able to press these soybeans after harvesting and make two distinct products, oil and meal. The meal is an instantly marketable product and can be sold as feedstock or organic fertilizer; the oil will be further processed into biodiesel.
Soybeans crops are well suited for biodiesel production in Vermont and perform best in heavy soil like those found in Addison County, as University of Vermont Extension Agronomist, Heather Darby explains. Soybeans don’t always do well in in light, well drained soils, and as with any crop the best way to understand the demands of any crops is to contact your University Extension and have your soil tested. Additionally, because soybeans are a legume, they produce nitrogen in association with bacteria, meaning that these crops don’t require the application of additional nitrogen to produce a high yield. These low input, high yield crops are fairly easy to grow, are well suited to the Vermont climate, and afford farmers flexible planting dates. Heather and the rest of the UVM Extension team have seen yields ranging from 35 bushels per acre to up to 85 bushels per acre with varying practices.
In the below video, Mike Mordasky shares his experience and knowledge of soybean production from planting through harvesting harvest and beyond to storage and the creation of the final products. In addition, Heather Darby shares here insights into maturity groupings, variety selection, and best growing practices.
Vermont’s solar industry is lauding Governor Peter Shumlin’s proclamation of the third Saturday in June as “Celebrate Solar Day” in Vermont.
The solar proclamation, announced at the Whitcomb Farm in Essex, coincides with this June 20th, when solar projects in communities throughout Vermont will be open for public tours. June 20 is the weekend of the Summer Solstice.
Like open sugarhouse weekend in the spring and open art studio weekend in the fall, the inaugural summertime tours will give Vermonters the opportunity to get an up-close view of solar systems to learn about the technology, solar economics, and the benefits of solar to our community. Solar customers, host farmers, and owners will be on-hand to speak with the public.
More than 50 systems across all regions of the state will be participating in Celebrate Solar Tours and a map of open tours can be found here. Many participating sites will host refreshments, music, or other entertainment. Other planned solar events include community walking tours of residential solar installations, miniature golf, a self-guided bike tour, and on-site yoga.
The Governor’s proclamation notes that “solar energy represented 99% of new electrical capacity in the state in 2014 and more than 5,000 Vermont customers have installed solar” through Vermont’s net metering program.
Further, it cites that the Vermont clean energy industries employ over 15,000 Vermonters, with solar providing “a broad spectrum of employment opportunities, helping retain and attract Vermonters working in manufacturing, installation, and sales, among other careers.”
The Whitcomb family is host to a 2.2 Megawatt solar farm that provides energy for Vermont’s SPEED program.
Among the solar sites open to tour June 20: iconic and sweet Vermont attractions like Cold Hollow Cider and Morse Farm Maple Sugarworks, high-tech attractions like Draker and Small Dog Electronics, agricultural farms like Champlain Orchards, shared community solar arrays, and some of Vermont’s highest producing solar farms.
At the announcement of the solar tours, Paul Brown, owner of Cold Hollow Cider in Waterbury Center, which has a 150kW system powering its operations, said of the event, “Folks know us and visit us for our cider and donuts. But we are thrilled to open up the field behind our cidery to share the benefits of solar technology to our business and our community. We’ll of course also be serving up some sweet treats for those who come by.”
About Celebrate Solar Tours – June 20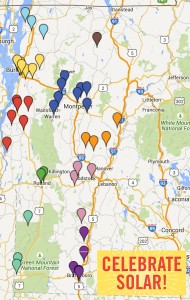
The first annual Celebrate Solar Tours on June 20 will feature public tours of more than 50 solar systems of varying size throughout the state. The public will have the opportunity to get an up-close understanding of the technology, economics and benefits to the community. Open systems will be designated with roadway signage and many will feature music, refreshments or other entertainment.
Contact: Ansley Bloomer
Ansley@revermont.org or 802-595-0723