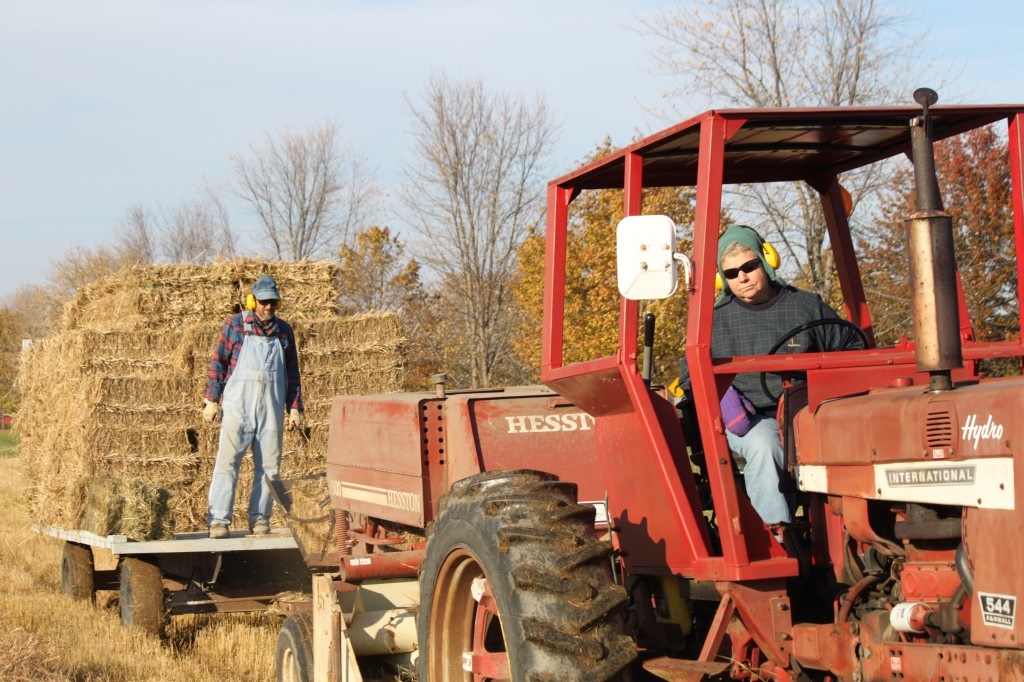
Baling switchgrass at Meach Cove Farm in Shelburne, Vermont. Photo Credit Vermont Bioenergy Initiative
Montpelier, VT – A new report evaluating grass biomass energy as a potential heating fuel has been released. Grass Energy in Vermont and the Northeast summarizes current research on the agronomy and usage potential of grass as a biofuel, and points to next steps for the region to fully commercialize this opportunity. The report was released last week by the Vermont Bioenergy Initiative, a program of the Vermont Sustainable Jobs Fund. The full report can be found on the Vermont Bioenergy Initiative website.
“There have been several independent assessments over the years of the various aspects of growing and burning grass for energy, but we were missing the step of linking it all together. We needed to put into one place what is currently known about grass energy, and get our remaining questions on paper,” says Sarah Galbraith, program manager of the Vermont Bioenergy Initiative. “It is very possible that grass as a heating fuel could enter into Vermont’s growing suite of renewable energy options. There are still uncertainties, but this report provides a series of recommendations and next steps for Vermont and the Northeast.”
The assessment for the report was conducted by members from Wilson Engineering Services and Ernst Conservation Seeds, and a former staff of Pennsylvania State University Cooperative Extension, who together conducted a literature review and interviews with experts in the field. The report was reviewed by the Vermont Agency of Agriculture, Food and Markets, University of Vermont Extension, Biomass Energy Resource Center, and the Vermont Sustainable Jobs Fund.

Grass for biofuels grow at the UVM Hort Farm in South Burlingon, Vermont. Photo credit Vermont Bioenergy Initiative
Grass Energy in Vermont and the Northeast includes key recommendations on models of grass energy that will work best for Vermont. Regional and closed loop processing were two models recommended, both involving farmers growing and harvesting grass, but differing in where the grass is processed into fuel and where it is used. The regional processing model calls for aggregating grass from a 50-mile radius at a central processing facility, where the grass is made into and used as fuel, or sold to local users. The closed loop model suggests farmers growing and processing grass on-site for on-farm or community use. Other models, like mobile on-farm processing and processing fuel for the consumer pellet market have significant hurdles to overcome if they are to be successful in Vermont.
Despite hurdles in some of the models presented, the report points to grass energy being a good option overall. “Native, warm-season grasses grown as a heating fuel are a viable energy crop for Vermont farmers wishing to diversify. Once the grasses are well-established, the input costs are minimal—especially compared to corn,” states Alexander DePillis, senior agriculture development coordinator for Vermont’s Agency of Agriculture, Food and Markets, an instrumental partner throughout planning for and publishing the grass energy report. “Grass thermal energy has the potential to help cut Vermont’s overall fuel bills while helping us meet the overall goal of the Comprehensive Energy Plan—for Vermont to obtain 90% of its energy from renewable sources by 2050.”
Perennial grasses can be grown on marginal lands not well suited for continuous row crop production and in open rural land currently not in agricultural production. The grass energy benefits reviewed in the report include retaining energy dollars in the local community, reducing greenhouse gas emissions from heating systems, improving energy security, providing a use for marginal farmland, and reducing pollution in soil and run-off from farms. Recommendations include a concerted effort in Vermont to plant grasses for energy on extended buffer strips along Lake Champlain, thereby reducing its nutrient load. Grass is a perennial crop harvested annually that can help level the increasing demand for forest biomass, while adding water quality and wildlife benefits by controlling erosion, reducing fertilizer use and providing cover and food for migrating and nesting birds.
In 2008, the Vermont Bioenergy Initiative began to explore the potential for grasses grown in Vermont to meet a portion of the state’s heating demand and reduce the consumption of non-renewable fossil fuels. The Grass Energy in Vermont and the Northeast report was initiated by the Vermont Sustainable Jobs Fund to aid in strategic planning for future grass energy program directives. The Vermont Bioenergy Initiative and subsequent grass energy report are funded by appropriations from the US Department of Energy secured by the Office of Senator Patrick Leahy.
The Vermont Bioenergy Initiative (www.vermontbioenergy.com) draws the connection between diversified agriculture and local renewable energy production for on-farm and community use. Aiming to supply farm inputs and reduce fossil fuel consumption, this program supports research, technical assistance, and infrastructure development in emerging areas of bioenergy. Since 2003 the program has focused on biodiesel production and distribution for heating and transportation, oil crops for on-farm biodiesel and feed, grass for heating, and algae production for biofuels and wastewater management. The Vermont Bioenergy Initiative is a program of The Vermont Sustainable Jobs Fund, a non-profit organization which provides financing, technical assistance and other resources to Vermont businesses who develop products and services and create jobs in the fields of renewable energy, and sustainable agriculture and forestry.
 The University of Vermont Extension Northwest Crops and Soils team held their annual Field Day on Thursday, August 1, 2013 from 10:00am to 3:30pm at Borderview Research Farm in Alburgh, Vermont.
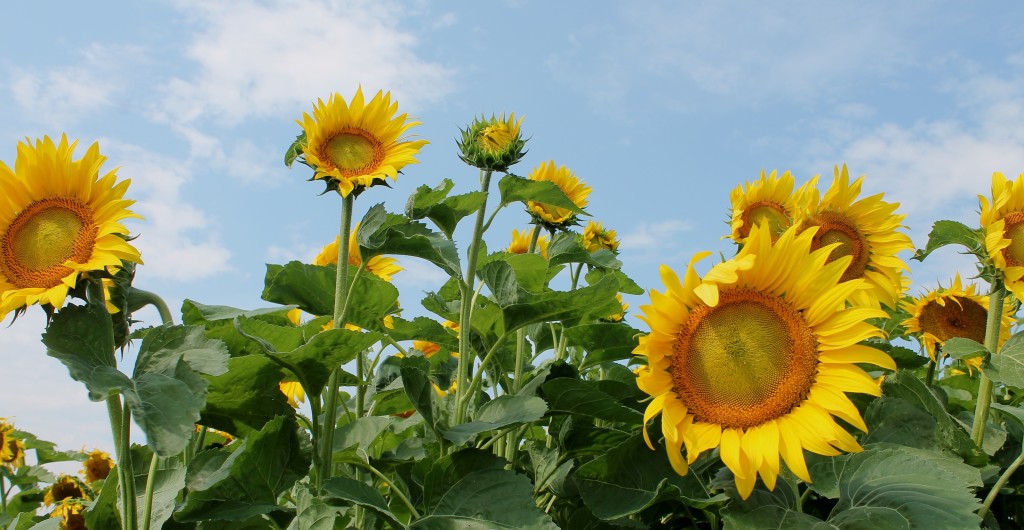
The University of Vermont Extension Northwest Crops and Soils team held their annual Field Day on Thursday, August 1, 2013 from 10:00am to 3:30pm at Borderview Research Farm in Alburgh, Vermont. om researchers and technicians focused on cover crops, irrigation systems, sunflowers for cooking oil and biodiesel, wheat varieties, aerial seeding, hops variety trials and demonstration of a mechanized hops harvester, and demonstration of an oilseed press.
om researchers and technicians focused on cover crops, irrigation systems, sunflowers for cooking oil and biodiesel, wheat varieties, aerial seeding, hops variety trials and demonstration of a mechanized hops harvester, and demonstration of an oilseed press.