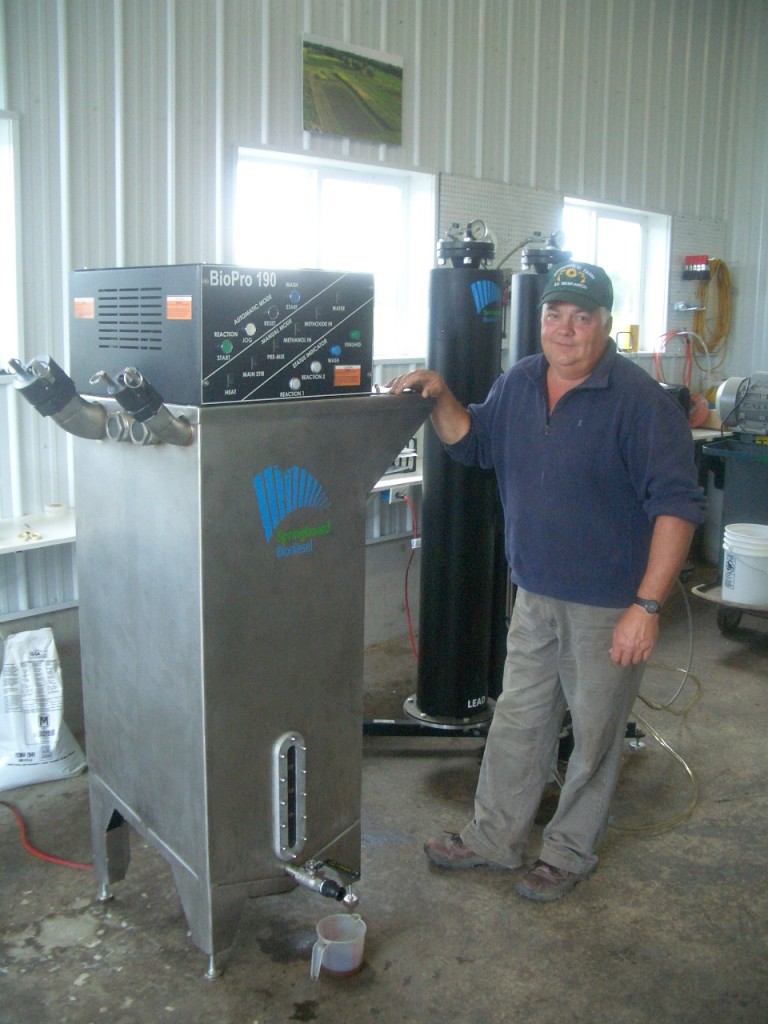
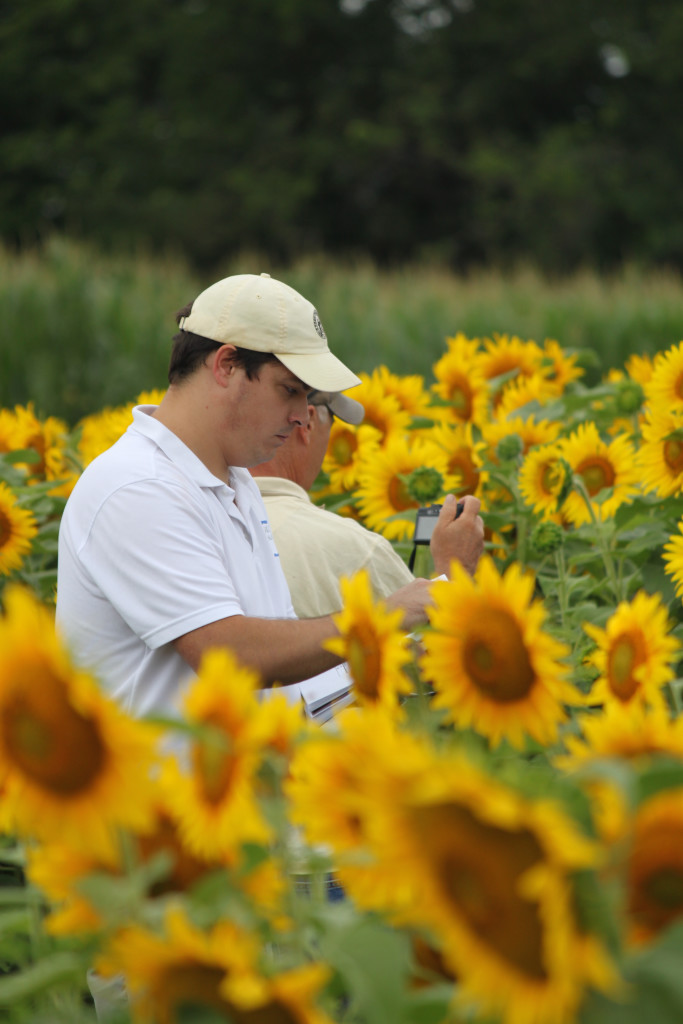
At Borderview Farm in Alburgh, Roger Rainville’s dairy-turned-energy farm makes biodiesel from locally-grown sunflower seeds.
At Borderview Farm in Alburgh, Roger Rainville’s dairy-turned-energy farm makes biodiesel from locally-grown sunflower seeds.
In 2008, when diesel prices rose from $4 to $5 per gallon, Rainville began experimenting with farm-scale biodiesel production. With guidance from UVM Extension and grant funding from the Vermont Bioenergy Initiative, Rainville began planting sunflowers on a portion of his 214 acres and installing biodiesel processing equipment. Oilseed sunflowers (as opposed to confectionary sunflowers that are grown for eating) are the most popular oilseed crop in Vermont, with hundreds of acres planted statewide. The crop is grown in rotation with grains and grasses and yields high quantities of oil.
Harvesting, Cleaning, and Pressing
Following harvest with a combine, a seed cleaner and grain dryer are used to prepare the seeds for storage in a 200-ton grain bin prior to processing. A flex auger system moves the seeds from the storage bin into hoppers on each press, and screw augers push the seed through a narrow dye at the front of the press. Extracted oil oozes from the side of the barrel and is collected in settling tanks while pelletized meal is pushed through the dye at the front and is stored in one-ton agricultural sacks. The oil can then be used as culinary oil for cooking or further refined into biodiesel. The leftover seed meal is used for livestock feed, fuel for pellet stoves, or fertilizer for crops.
Biodiesel Processing
The small-scale biodiesel production facility at Borderview Farm is an 800 square foot insulated and heated building (the space does not need to be heated, but the oil should be stored where it will not freeze) that houses an oil press, a BioPro 190 automated biodiesel processor, a methanol recovery system, and a set of dry-wash columns for cleaning the fuel. The clean oil at the top of each settling tank is added to the BioPro 190 processor along with lye, methanol, and sulfuric acid. The automated processor runs through several stages of processing in about 48 hours (esterification, transesterification, settling, washing, and drying), with one break after 24 hours to remove the glycerin byproduct.
Safety equipment in the processing facility includes personal protective equipment like aprons, gloves, eye protection, a ventilation system, gas detectors, and spill containment materials. At Borderview Farm a set of standard operating procedures hangs on the wall and blank check-sheets are in a binder to make the process easy to repeat. The finished biodiesel is stored in 250 gallon pallet tanks making distribution to different farms easier. The installed capacity of the facility can process 100 tons of seeds from 138 acres of sunflowers per year, yielding 10,500 gallons of biodiesel and 64 tons of sunflower meal (assuming the state average yield of 1,500 pounds sunflower seeds per acre and operation of 24 hours per day for 260 days per year).
Rainville switched from purchasing diesel for five tractors and one truck to making his own biodiesel. He wanted to be independent of imported fuel, and liked creating a new way for farmers to diversify. “Using land for making biodiesel is not the most economical option compared to some other crops, but it’s about creating opportunities to try something different,” says Rainville.
Cost Benefits
Rainville’s annual biodiesel use has ranged from 500 to 3,000 gallons per year. At current prices (over $4 per gallon for diesel and $2.29 per produced gallon of biodiesel) biodiesel has saved him from $500 to $4,000 per year in fuel costs. He also emphasizes energy independence as an added benefit. Plus, any growers that also raise livestock can use the meal, which is leftover after the oil is extracted, as part of their feed rations. Rainville recommends talking with an animal nutritionist to blend this into feed at the right ratio, since sunflower meal has a high fat content.
This story was originally released in a series of energy case studies showcasing farms, businesses, vendors, installers, and technical assistance providers who have made a difference with energy efficiency savings and renewable energy production—all of which are components for helping Vermont reach the renewable energy and environmental impact goals of the Farm to Plate Strategic Plan. Learn more at www.vtfarmtoplate.com.
02 Nov 2015
Vermont Bioenergy Initiative proves biofuel potential for state and concludes ten year project
By: Ellen Kahler

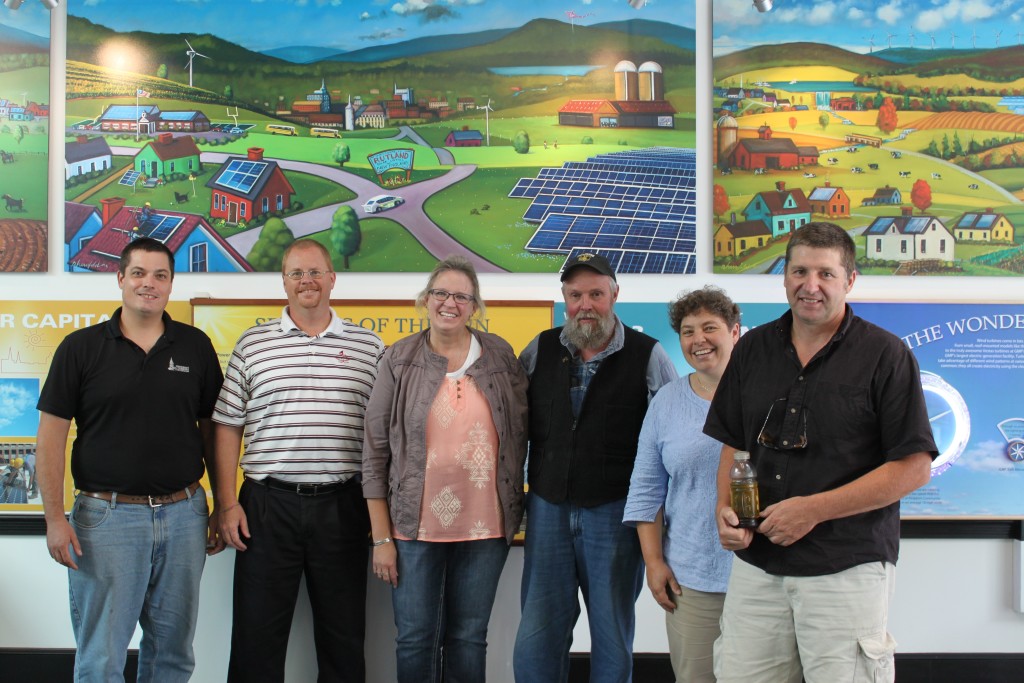
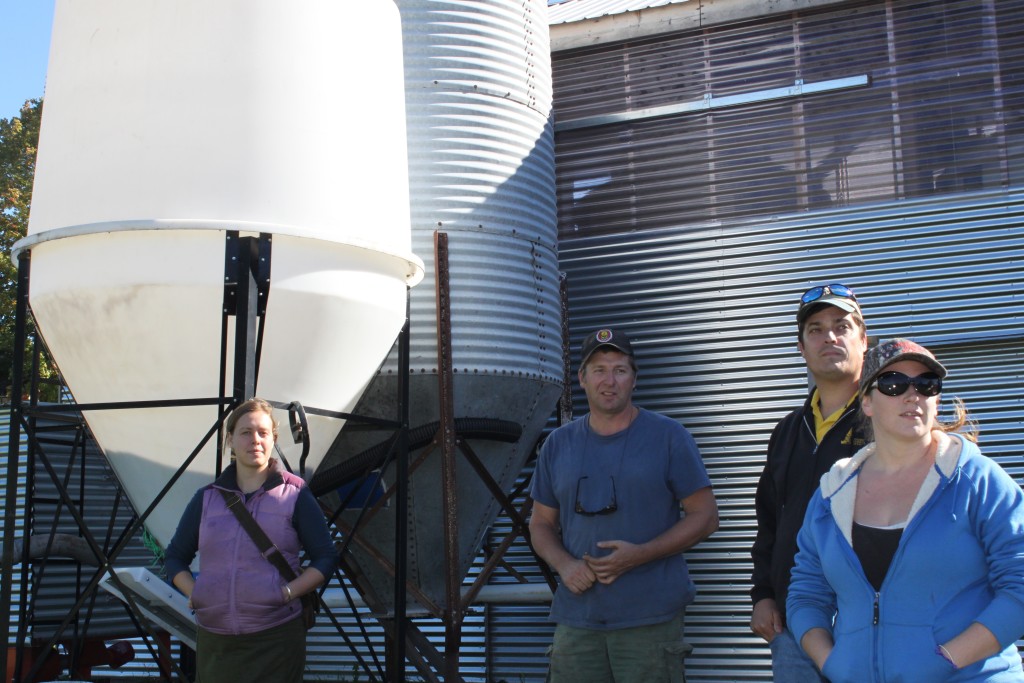
VT Bioenergy Team – L to R (Chris Callahan – UVM Extension, Kirk Shields — Green Mountain Power, Christy Sterner – US DOE, Larry Scott – Ekolott Farm, Ellen Kahler – VSJF, John Williamson – Stateline Biofuels) at Green Mountain Power’s Energy Innovation Center in Rutland
Vermont can produce more of its own biofuel energy and the environmental and potential economic benefits of local bioenergy have been proven by the Vermont Bioenergy Initiative – a program of the Vermont Sustainable Jobs Fund. Since 2005, the Vermont Bioenergy Initiative has invested more than $2.5 million in innovative bioenergy research, projects, and people so Vermont can locally produce more of the state’s energy needs – from a variety of agricultural and algal feedstocks.
US Senator Patrick Leahy made the investment at this scale possible through Congressionally Directed Awards from the US Department of Energy (US DOE). The funding concludes in early 2016, at which point a complete impact report will be released by the Vermont Sustainable Jobs Fund, who has served as the intermediary between the US DOE and 52 individual Vermont bioenergy projects over the past ten years.
Research, development, and early stage demonstration projects have included:
- Investing in 2 on-farm methane digesters;
- Building farm-scale infrastructure to turn oilseed crops such as sunflowers into biodiesel to run farm tractors;
- Growing switchgrass and densifying it into “pucks” that are burned in a high efficiency commercial boiler instead of propane;
- Identifying the most lipid producing strains of native Vermont algae which can feed off the excess nutrients from methane digesters and can eventually be harvested to make biodiesel or jet fuel;
- Developing two “Biomass to Biofuels” college level courses which run repeatedly at UVM and VT Tech to inspire and train the next generation of bioenergy experts and technicians;
- Exploring the logistics of bulk wood pellet delivery systems to Vermonters’ homes;
- Organizing a number of learning opportunities and conferences for oilseed, grass and algae researchers, farmers and entrepreneurs to attend;
- Providing agronomic and engineering support to oilseed and grass farmers;
- Educating the general public about why the local production for local use of energy crops from Vermont farms and forests makes good economic and ecological sense.

VT Bioenergy Team 2 – L to R (Roger Rainville – Borderview Farm, Christy Sterner – US DOE, Heather Darby – UVM Extension, Natasha Rainville – Borderview Farm) at Borderview Farm, Alburgh VT
The Vermont Bioenergy Initiative is a unique effort and one that is gaining resonance in other parts of rural America. The initiative’s resource website, www.VermontBioenergy.com is utilized by biofuel producers, educators, and technical service providers from across the country.
The work conducted over the past ten years by the Vermont Bioenergy Initiative to conduct research, provide technical assistance, and develop infrastructure in emerging areas of bioenergy will continue with the initiative’s partners at UVM Extension and the Vermont Agency of Agriculture, Food & Markets. As Vermont moves forward – being innovative and increasingly focused on generating renewable energy from the land and forests – the research and infrastructure the Vermont Bioenergy Initiative has invested in over the past ten years will endure and spawn the next wave of bioenergy development in the state.
Ellen Kahler is executive director of the Vermont Sustainable Jobs Fund (VSJF), a non-profit organization created by the State of Vermont to help develop Vermont’s sustainable agriculture, renewable energy, and forest product businesses. Since 2005, the Vermont Bioenergy Initiative has been a VSJF program that connects diversified agriculture and local renewable energy production for on-farm and community use by supporting research, technical assistance, and infrastructure development in emerging areas of bioenergy including biodiesel production and distribution for heating and transportation, oil crops for on-farm biodiesel and feed, grass for heating, and algae production for biofuels and wastewater management. Learn more at www.VermontBioenergy.com.
 David Marchant and Jane Sorensen of River Berry Farm—an organic vegetable and fruit producer in Fairfax—were early adopters of biomass heating when they installed a corn and pellet furnace in one of their greenhouses in 2008. The furnace required manual lighting and was snuffed out often when strong winds blew, and did not produce reasonable heat. “I kept thinking, there has got to be a better option,” recalls David, “It was a real labor burden, and you couldn’t count on it.”
David Marchant and Jane Sorensen of River Berry Farm—an organic vegetable and fruit producer in Fairfax—were early adopters of biomass heating when they installed a corn and pellet furnace in one of their greenhouses in 2008. The furnace required manual lighting and was snuffed out often when strong winds blew, and did not produce reasonable heat. “I kept thinking, there has got to be a better option,” recalls David, “It was a real labor burden, and you couldn’t count on it.”
Based on their early experiences and bolstered by a commitment to long-term sustainability and reduced fossil fuel dependence, River Berry Farm opted to host a biomass heating demonstration project. This time, they opted for a higher-rated boiler rather than a furnace. Boilers produce hot water, rather than hot air, which allows more options for distributing the heat. The new system also had an automated propane ignition system.
The biomass heating demonstration was part of a UVM Extension project aimed at trialing several furnaces in agricultural heating applications with funding support provided by the High Meadows Fund. According to Chris Callahan, Ag Engineer with UVM Extension Agricultural Engineering Program who assisted with some of the design and performance assessment, “The main lessons learned from these early installations were to buy high quality fuel, seek improved automatic ignition controls, invest in a good chimney and install it well, and know the actual heat output rating of the unit.”
Modern biomass heating appliances generally include a fuel storage bin, an auger for feeding fuel to the appliance, the appliance itself (boiler or furnace) with an ignition system, a combustion chamber, a heat exchanger, and a heat distribution system. They also incorporate some means of controlling combustion, fuel feed rate, and air flow and often include emissions control measures and automated ash removal.
The selected boiler was a Central Boiler Maxim 250 with a 250,000 BTU/hr input rating, efficiency of 87.8%, and EPA Phase II Hydronic Heater qualification. “The boiler makes hot water which we can use in multiple greenhouses by plumbing it to them in insulated PEX piping. Once in the greenhouse, we convert to hot air with a hot water fan coil, put it in the ground for root-zone heating or on the benches in our mat-heating system for starts,” says Marchant. “I like it. I keep trying to find something wrong with it, but I can’t. The payback period is a bit longer due to higher initial costs, but you have to expect that.”
The basic system cost was approximately $13,000 for the boiler, bin, pad, and plumbing to a hot water fan coil. The other heat distribution systems included in-ground PEX, heat exchange, and plumbing for a bench heat system and added approximately another $5,000. The system is more automated and reliable than the earlier furnace was, but the higher initial costs and the fact that the system is only used 3 months out of the year do prolong the payback period to about 12 years when compared with a propane furnace. If the system was used for 6 (space heating) or even 12 months (wash water, pasteurization) of the year the payback would be halved or quartered, respectively.
“In addition to the financial payback, the carbon emissions avoidance is also of interest to many people,” says Callahan, “In River Berry Farm’s case, the Maxim is helping them avoid 5,910 pounds of net CO2 emissions per year which is about equivalent to 5,000 miles car travel or the CO2 sequestered by half an acre of pine forest.”
Learn more about UVM Extension’s Agricultural Engineering Program at.
This story was originally released in a series of energy case studies showcasing farms, businesses, vendors, installers, and technical assistance providers who have made a difference with energy efficiency savings and renewable energy production—all of which are components for helping Vermont reach the renewable energy and environmental impact goals of the Farm to Plate Strategic Plan. Learn more at www.vtfarmtoplate.com.
 Efficiency Vermont, Renewable Energy Resource Center, Renewable Energy Vermont and Clean Energy Development Fund combine efforts to bring up to $5,500 in rebates to Vermonters who heat local
Efficiency Vermont, Renewable Energy Resource Center, Renewable Energy Vermont and Clean Energy Development Fund combine efforts to bring up to $5,500 in rebates to Vermonters who heat local
Through a generous opportunity, Vermonters now have a short-time frame before the new year to capitalize on a fantastic incentive offering that helps them save money, while supporting Vermont jobs and sustainable forests, while making sure they stay warm this winter.
Vermonters can get up to $5,500 to help switch from fossil fuel to local wood heating. Cash incentives are available from the Clean Energy Development Fund and Efficiency Vermont. Renewable Energy Vermont and the Renewable Energy Resource Center have partnered to help promote the incentives.
“We’ve been very happy with our decision to switch to a wood pellet boiler. Not only do we save money every year on our fuel bill, but we also love the fact that we’re helping to keep forests intact and logging jobs going,” says Mark Bushnell of Middlesex.
Vermonters who make the switch to wood pellet fuel typically save $1,500 annually when compared to oil and propane fuel heating options. And for those who are used to whole-home heating through their traditional boiler, the wood pellet boiler keeps it simple and complete. Advanced wood pellet boilers are fully automatic, so there’s no work for the home or business owner.
“I heated my home for years with a standard wood stove, but I’m happier with my wood pellet boiler. The new boiler is much more efficient and better for the environment because it is cleaner burning. And it feels great to be off fossil fuels,” says Susan Clark of Middlesex.
Wood pellet boilers, though not well known in the United States, are the primary way of heating in some parts of the world, including Upper Austria where more than 40,000 homes and businesses heat with wood from their background in an easy, seamless way. In fact, the State of Vermont and Upper Austria are involved in a Sister Statehood Agreement to help learning across both sides of the Atlantic to increase the uptake of this sustainable, local heating option.
“For many years, Vermont has been a national leader in the use of modern wood heating systems in large buildings like schools, office buildings, and apartment buildings. With pellets now available in bulk using specialized delivery trucks that conveniently blow pellets into a fuel bin and heating systems that are fully-automated, many homeowners and small businesses are also making the switch from oil and propane,” said Adam Sherman of the Biomass Energy Resource Center.
For more information, please go to www.advancedwoodheat.com
Media Contacts:
Renewable Energy Vermont, Ansley Bloomer, ansley@revermont.org (802) 595-0723
Biomass Energy Resource Center, Alayna Howard, ahoward@veic.org (802) 540-7656
Renewable Energy Resource Center, Alayna Howard, ahoward@veic.org (802) 540-7656
Efficiency Vermont, Alayna Howard, ahoward@veic.org (802) 540-7656
Clean Energy Development Fund, Andrew Perchlik, andrew.perchlik@state.vt.us (802) 828-4017
The Vermont Bioenergy Initiative connects diversified agriculture and local renewable energy production for on-farm and community use by supporting research, technical assistance, and infrastructure development in emerging areas of bioenergy including biodiesel production and distribution for heating and transportation, oil crops for on-farm biodiesel and feed, grass for heating, and algae production for biofuels and wastewater management. Explore the initiative’s extensive and accessible set of bioenergy resources for replication in rural communities across the United States and beyond.
Video
A series of informative educational showcase a range of biofuel possibilities; from research and crop farming to feedstocks and fuel. The videos were developed by the Vermont Sustainable Jobs Fund, UVM Extension researchers, KSE Partners, and the Vermont Bioenergy Initiative grantees.
Calculators
Two calculators, developed by UVM Extension, help connect potential costs and profits associated with oilseed production:
- Grass Biomass Production and Harvest Cost Estimator
- Vermont Oilseed Crop Production Cost and Profit Calculator
Course Work
- Biomass to Biofuels, University of Vermont: This semester-long course covers liquid and solid biofuels, biogas and bio-electricity, and environmental, social and economic issue related to biofuels. The course includes guest lecturers and field days. Available for variable credits.
- Biomass to Biofuels, Vermont Technical College: The development of this course and associated materials led to an online repository of resources for the classroom covering biomass to biofuels.
- Digester Operations Master Certificate, Vermont Technical College: a twelve week program designed for participants to work directly with operations staff of Vermont Tech’s anaerobic digester and come away with understanding of the mechanics and operations of a digester system, as well as other areas such as permitting, regulatory compliance and record keeping.
- Alternative Fuel Vehicles: Biodiesel, part of the Green Trainings series at Vermont Technical College: This 2-day course covers engine systems, biodiesel blends and biodiesel production, including a demonstration of fuel-making equipment.
- Biofuels Course at Yestermorrow Design/Build School, part of the Green Trainings series at Vermont Technical College: This weekend workshop enables students to begin replacing fossil fuels with biofuels, such as adapting engines to run on straight vegetable oil. 1 credit.
Textbook
Bioenergy: Biomass to Biofuels; is an innovative new textbook that provides insight into the potential and current advances and benefits of biofuel. Contributions include an extensive list of well-respected university extension programs, such as The University of Vermont Research Extension, as well as numerous national organizations including the US Department of Energy’s National Renewable Energy Laboratories.
Reports
A variety of reports are available which cover a range of topics including seed preparation and storage:
- Institute for Energy and the Environment at Vermont Law School.Legal & Regulatory Review of On-farm Biodiesel Production. 2015.
- Chris Callahan and Netaka White,Vermont On-Farm Oilseed Enterprises: Production Capacity and Break-even Economics. July 2013.
- Nell Campbell, Local Production for Local Use to Supply a Portion of Vermont’s Energy Needs.May 2009.
- Emily J. Stebbins. Technical and Economic Feasibility of Biodiesel Production in Vermont: Evidence From a Farm-Scale Study and a Commercial-Scale Simulation Analysis. May 2009.
- Christopher W. Callahan,A Feasibility Analysis of a Mobile Unit for Processing Oilseed Crops and Producing Biodiesel in Vermont. December 2008.
- Emily Stebbins, The Market Potential of Farm-Scale Oilseed Crop Products in Vermont. February 2008. (See also the Executive Summary)
- John Williamson & Tanner Williamson – State Line Biofuels, LLP, Chris Callahan – Callahan Engineering, PLLC, Feasibility Analysis:_Solar Seed Dryer and Storage Bin at State Line Farm, Bennington, VT. October 2008
- Christopher W. Callahan, A Feasibility Study of a Mobile Unit for Processing Oilseed Crops and Producing Biodiesel in Vermont. December 2008
- Kenneth Mulder, Ph.D., Galen Wilkerson, Emily J. Stebbins.Homegrown Fuel: Economic Feasibility of Commercial-Scale Biodiesel Production in Vermont. September 2007.
- The Vermont Biodiesel Project: Building Demand in the Biofuels Sector – Final Report. October 2006. (See also theExecutive Summary)
- Vermont Department of Buildings and General Services, Vermont Biodiesel Pilot Project: Emissions Testing of Biodiesel Blends With #6 Fuel Oil At the Waterbury State Office Complex – Final Report. September 2006.
- Laboratory and Field Testing of Biodiesel in Residential Space Heating Equipment – Final Report. August 2006.
- Vermont Biodiesel Supply Chain Survey – Final Report. April 2006.
- Wilson Engineering,Grass Energy in Vermont and the Northeast, May 2014.
Technical Advice
Connect directly with the Vermont Bioenergy Initiative’s technical assistance providers:
Oilseeds for Biofuel
- Heather Darby, Agronomic and Soils Specialist
- University of Vermont Extension, Northwest Crops and Soils Team
- (802) 524-6501
- darby@uvm.edu
- Chris Callahan, PE, Agricultural Engineer
- University of Vermont Extension
- (802) 773-3349
- callahan@uvm.edu
Grass for Heating Fuel
- Sidney Bosworth, Extension Professor
- University of Vermont College of Agriculture and Life Sciences
- (802) 656-0478
- bosworth@uvm.edu
Algae for Biodiesel
- Anju Dahiya, Instructor and Principal
- University of Vermont and GSR Solutions
- (802) 310-1936
- adahiya@uvm.edu
10 Aug 2015
Bioenergy Events 2015
The team  at Vermont Bioenergy Initiative has worked to put together a comprehensive list of bioenergy events for you! This list will be updated as more events arise. If you know a bioenergy events that you think should be on the list, tweet it to us! @VTbioenergy
at Vermont Bioenergy Initiative has worked to put together a comprehensive list of bioenergy events for you! This list will be updated as more events arise. If you know a bioenergy events that you think should be on the list, tweet it to us! @VTbioenergy
- September
- Modern Wood Pellet Heating Forum, Tuesday, Sep. 15, 2015, 6 – 8:30pm, Montshire Museum in Norwich, Vermont
- Ag Innovation Showcase September 14-16, 2015 St. Louis, MO
- 2nd International Conference on Past and Present Research Systems of Green Chemistry. September 14-16, 2015. Orlando, Florida
- Switchgrass III. September 30 to October 2, 2015. Knoxville, TN
- Algae Biomass Summit September 30-October 2, 2015 Washington, DC
- October
- Renewable Energy 2015 Conference & Expo. October 8-9 2015. Burlington, VT
- National Advanced Biofuels Conference & Expo. October 26 – 28, 2015. Omaha, Nebraska
- 2015 TAPPI PEERS Conference – Sustainable Solutions for Our Future. October 25-28, 2015 in Atlanta, Georgia.
- International Bioenergy and Bioproducts Conference 2015 – 10/28 – 10/30 Atlanta, United States
- 3rdAnnual National Bioenergy Day
- November
- April
In order to meet the goals set by Vermont’s comprehensive energy plan for Vermont to produce 90 percent of the state’s energy needs from renewables by 2050 and reduce Vermont’s greenhouse gas emissions by 50 percent from a 1990 baseline, Vermont farmers will have an important role to play. As Vermont experiences growth in food-related businesses and jobs, decisions about energy become more important prompting statewide energy and agriculture collaborations. In the following episodes of Across the Fence, UVM Extension agricultural engineer and Vermont Bioenergy Initiative biofuels consultant, Chris Callahan, shares two stories about Vermont farmers who are rethinking their on-farm energy. In both examples UVM extension is able to work with the farmers to help make cleaner, renewable on-farm energy sources a practical solution that saves money and results in greenhouse gas reductions.
Learn more in a series of on-farm energy case studies produced by Vermont’s Farm to Plate Initiative.
 Coming this fall the University of Vermont will be offering a bioenergy course taught by Anju Dahiya, cofounder of General Systems Research, LLC, lead biofuels instructor at the University of Vermont’s Rubenstein School of Environment and Natural Resources, and Vermont Bioenergy algae for biofuel grant recipient. This course is open to both degree and non-degree students from any background or department, as well as farmers, entrepreneurs, and teachers interested in developing curriculum, or projects at school or college levels. This course is also approved for graduate credit.
Coming this fall the University of Vermont will be offering a bioenergy course taught by Anju Dahiya, cofounder of General Systems Research, LLC, lead biofuels instructor at the University of Vermont’s Rubenstein School of Environment and Natural Resources, and Vermont Bioenergy algae for biofuel grant recipient. This course is open to both degree and non-degree students from any background or department, as well as farmers, entrepreneurs, and teachers interested in developing curriculum, or projects at school or college levels. This course is also approved for graduate credit.
Potential participants are offered the option of variable credits, ranging from 0 to 6 credit hours. This allows prospective students to only attend lectures and have access to online course materials for 2 credits; further their experience with the addition of hands-on labs and field trips for 3 credits; or participate in all aspects of the class while additionally applying lessons to a service learning project with a community partner, earning 4 credits. Participants have the ability to add up to 2 more credits, totaling no more than 6, for additional work with the community partner pending special permission from the course instructor.
 Lectures will be held twice a week between September 18th and December 9th of 2015. Friday lectures will be on campus from 4:05 pm to 7:05 pm, followed by Saturday morning field trips between 10:00 am and 1:00 pm for those students who elected for 3 credits or more. The course required textbook, Bioenergy: Biomass to Biofuels, was edited by Anju Dahiya less than a year ago and represents a compilation of work from an extensive list of well-respected university extension programs, such as The University of Vermont Research Extension, as well as numerous national organizations including the US Department of Energy’s National Renewable Energy Laboratories.
Lectures will be held twice a week between September 18th and December 9th of 2015. Friday lectures will be on campus from 4:05 pm to 7:05 pm, followed by Saturday morning field trips between 10:00 am and 1:00 pm for those students who elected for 3 credits or more. The course required textbook, Bioenergy: Biomass to Biofuels, was edited by Anju Dahiya less than a year ago and represents a compilation of work from an extensive list of well-respected university extension programs, such as The University of Vermont Research Extension, as well as numerous national organizations including the US Department of Energy’s National Renewable Energy Laboratories.
Learn more about this course at the University of Vermont Renewable BioEnergy page or email the lead instructor Anju Dahiya at adahiya@uvm.edu.
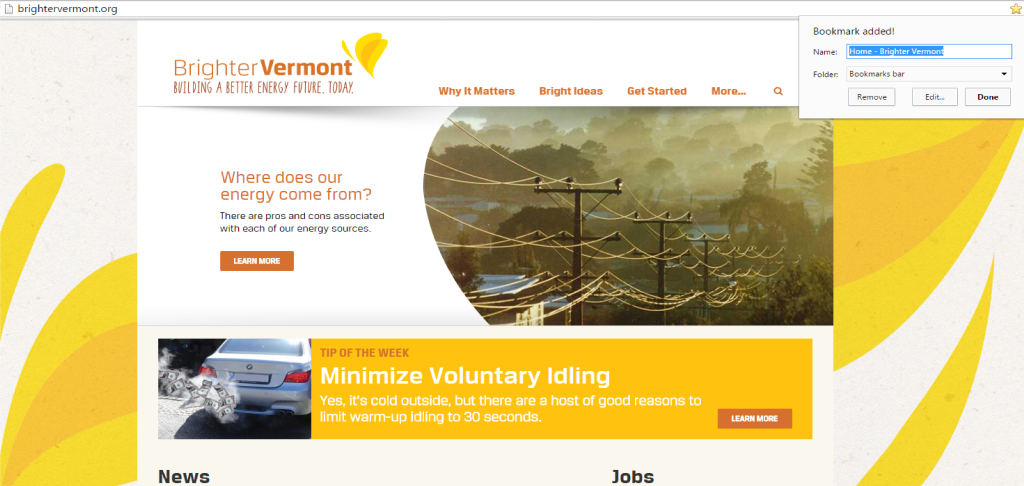
The EAN’s 4 Key Leverage Points of capital mobilization, public engagement, technology innovation, and regulatory reform
The Energy Action Network (EAN) is a community of a community of Green Mountain State stakeholders working to change the Vermont energy landscape “to end Vermont’s reliance on fossil fuels and to create clean, affordable energy and secure electric, heating, and transportation systems for the 21st century.” Their goals are consistent with the State of Vermont 2011 Comprehensive Energy Plan, which aims to meet 90% of Vermont’s energy needs through efficiency and renewable sources by 2050.
EAN has identified a series of pathways for Vermont for Vermont to accomplish the paradigm shift of 90% renewables by 2050. Membership is structured into working groups focused on four “leverage points” capital mobilization, public engagement, technology innovation, and regulatory reform. Current projects include alterations to Act 250, changes in zoning laws, programs to promote bringing rental properties into efficiency standards, and assessing current land use for its potential for bioenergy and solar projects.
One notable awareness vehicle, Brighter Vermont, encourages Vermonters to change the way common energy use and think more about where energy comes from. Read more about how Brighter Vermont helps change energy behavior. EAN also works with municipalities and recently helped Montpelier plan for a 15 year track to become the first state capital to accomplish all of its energy needs with renewable energy. On February 12, 2015 the Montpelier City council accepted and endorsed the plan to make Montpelier a “net zero” city.
Currently, EAN is working with the Vermont Sustainable Jobs Fund to expand the Vermont Energy Atlas website into the Community Energy Dashboard. The Dashboard will enable communities to understand their energy use and make clean energy choices and investments across all energy sectors—heating, transportation, and electricity. The Dashboard will make energy use visible and understandable to consumers and communities by showing town-level progress toward Vermont’s 90% renewables by 2050 goal. The Dashboard will also shows existing and potential renewable energy sites (solar, wind, hydro, biomass). We will provide updates as they develop. Stay tuned into the Vermont Bioenergy Field Notes blog and visit the Energy Action Network website to learn more.
20 Apr 2015
Getting Smart About Vermont Energy
 The State of Vermont 2011 Comprehensive Energy Plan calls for 90% of Vermont energy needs to be met through efficiency and renewable sources by 2050. As Vermont residents witness continued high numbers in clean energy jobs, and advanced renewable energy legislation they will also need to take responsibility for Vermont to meet these goals, as every Vermonter will need to contribute in some way for Vermont to meet this ambitious goal. Enter Brighter Vermont, an action oriented program of the Energy Action Network, to help everyday Vermonters rethink where their energy comes from, how they use it in their daily lives, and what they can do to help the state reach its 90% by 2050 goal.
The State of Vermont 2011 Comprehensive Energy Plan calls for 90% of Vermont energy needs to be met through efficiency and renewable sources by 2050. As Vermont residents witness continued high numbers in clean energy jobs, and advanced renewable energy legislation they will also need to take responsibility for Vermont to meet these goals, as every Vermonter will need to contribute in some way for Vermont to meet this ambitious goal. Enter Brighter Vermont, an action oriented program of the Energy Action Network, to help everyday Vermonters rethink where their energy comes from, how they use it in their daily lives, and what they can do to help the state reach its 90% by 2050 goal.
The Brighter Vermont website is packed with testimonials and videos shared by individuals who describe the financial decisions they are making to positively affect the environment, Vermont’s economy, and their wallets. A family in Rutland reports on small home improvement they have made to keep out the Northeast cold out and share a video about lowering energy costs, with the help of Green Mountain Power, by properly weatherizing their home, changing to energy efficient LED bulbs, electing for a heat pump, and adding solar panels. The overall transition has made them a more energy conscious family and was achievable with a ten year loan the family is pleased to see being offset by reduction in energy costs.
A family in Burlington’s journey towards reducing their carbon footprint is documented in a fun testimonial video where the family picks out their first electric vehicle. They were able to replace one of their family vehicles with a zero emission Nissan Leaf (hyperlink to video) that was available with an affordable two year lease. The switch from a classic Vermont staple vehicle, a Subaru, to the Leaf, has helped the family not only save money at the gas pump, but the, as the family reports, electricity used to charge the vehicle comes from renewable energy. They enjoy educating their friends and neighbors about this carbon footprint transition.
Brighter Vermont also hosts ways for businesses, schools, and towns to become more efficient and promote renewables in their community. Methods for how schools and businesses have become more efficient by transitioning to modern wood heating. A featured video produced by VEIC (hyperlink) features 54 schools from across Vermont currently heating with wood chips and pellets which provides heat for nearly one third of k-12 students across Vermont. Our own Vermont Bioenergy Initiative Vermont on-farm energy videos are also featured for farmers to learn more about the emerging areas of oilseed, grass, and algae biofuel.
There is much that needs to be done in the fight against climate change and moving Vermont away from its reliance on fossil fuels. While this road can be daunting, it is important to remember that we can all make small changes that will benefit us, our community, and our state. And the Brighter Vermont website provides a fun and interactive platform for individuals, families, businesses, and institutions to learn how to contribute and share these efforts with others so Vermont can take steps towards meeting our renewable energy goals for our future.