01 Jun 2015
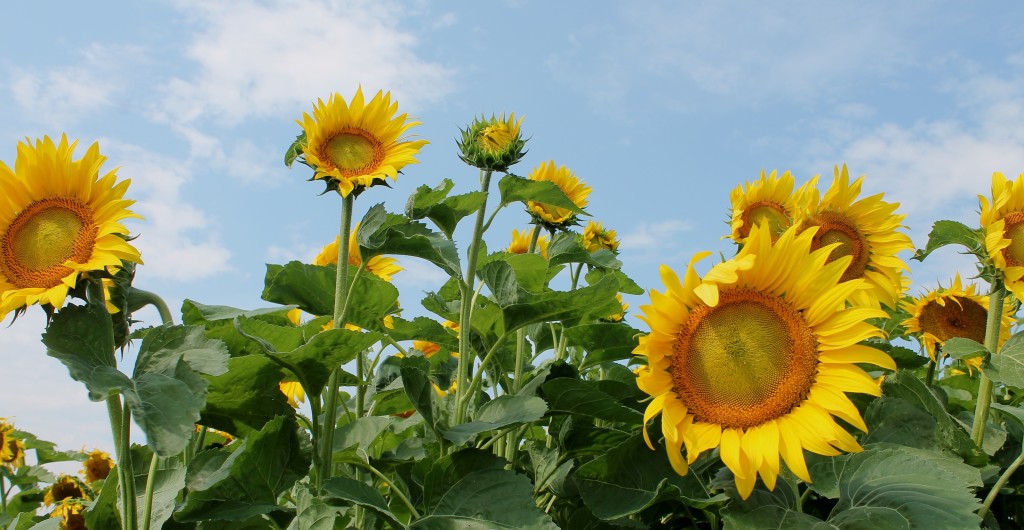
Food Versus Fuel – Local Production for Local Use – Biodiesel as Part of Sustainable Agriculture
Nationally, corn-based ethanol and palm oil based biodiesel are gaining negative attention for their impacts on the environment and food security. But here in Vermont, farms are producing on-farm biodiesel to power equipment and operations on the farm and the local farm community. This is a profoundly different model from national and international biofuel production. Agricultural Engineering and Agronomy Researchers at University of Vermont Extension in partnership with farmers and the Vermont Bioenergy Initiative have developed a model of local minded, on-farm production of biofuels that can help rural communities transition away from unsustainable models of food, feed and fuel production.
National and global models of corn-ethanol and soy oil-biodiesel production are resulting in large-scale land conversions in some parts of the world, in particular to a loss of native grass and forestland. This type of biofuel production is not happening in Vermont, where bioenergy production incorporates rotational oilseed crops like sunflowers and soybeans on Vermont farms.
Locally produced biodiesel supports resiliency in Vermont, a cold climate state which is particularly dependent on oil. Over $1 billion leaves the state for heating and transportation fuel costs. Heating and fuel independence by producing on-farm biodiesel provides farmers fuel security which is comparable to that which is sought by Vermont’s local food movement.
The local production for local use model results in two products from one crop: oil and meal (animal feed or fertilizer). By growing oilseed and pressing the seed to extract the oil, farms are creating a valuable livestock feed at home, rather than importing it. The oil can be sold as a food product, used directly in a converted engine or converted to biodiesel for use in a standard diesel engine. In this way, oilseed crops offer flexibility in the end-use of the products. US corn-based ethanol mandates are raising grain costs nationally, making feed expensive for Vermont farmers. Local bioenergy production means farmers produce their own feed, fuel, and fertilizer for on-farm use, at a fraction of the cost and more stable prices. Reduced and stable prices for feed, fuel, and fertilizer can mean improved economic viability for Vermont farms and more stable food prices for Vermont consumers in the future.
Overall viability can be seen in the local production for local use model by considering economics, energy and carbon emissions. Biodiesel production costs of between $0.60 and $2.52 per gallon have been estimated for farm-scale production models, which are generally below market price for diesel fuel. The net energy return in Vermont on-farm biodiesel operations has been estimated at between 2.6 and 5.9 times the invested energy (i.e. more energy out than was required to produce the fuel), demonstrating strong returns and potential for improvement with increased scale. Furthermore, oilseed-based production of biodiesel has been estimated to result in a net reduction of carbon dioxide emissions of up to 1420 lbs. per acre, the equivalent of about 1500 miles of car travel per year.
Categorizing the Vermont biofuel model with national models and trends is inaccurate, considering the innovative and efficient systems benefiting Vermont farmers. While national and international analysis weighs the benefits of food versus fuel, the model is quite unique in Vermont and the food versus fuel challenge is well met. The model developed in Vermont does however have wider-reaching implications in that this can be replicated in rural farm communities across the US.
As John Williamson of Stateline Farm, a Vermont Bioenergy grant recipient says, “100 years ago everyone produced their own fuel; we are just doing that now in a different way.”
19 May 2015
Mitigating Potential Biomass Feedstock Pests
The Vermont Bioenergy Initiative aims to connect diversified agriculture and local renewable energy production for on-farm and community use by supporting research, technical assistance, and infrastructure development in emerging areas of bioenergy including biodiesel production and distribution. As we move into the growing season, there are a variety of pests that can potentially affect sunflower, canola, and soybean biomass feedstock production. In this video a University of Vermont agronomist explains how to control theses potential biomass feedstock pests and increase crop, and eventually biofuel, yields without heavy reliance on pesticides and herbicides.
 Coming this fall the University of Vermont will be offering a bioenergy course taught by Anju Dahiya, cofounder of General Systems Research, LLC, lead biofuels instructor at the University of Vermont’s Rubenstein School of Environment and Natural Resources, and Vermont Bioenergy algae for biofuel grant recipient. This course is open to both degree and non-degree students from any background or department, as well as farmers, entrepreneurs, and teachers interested in developing curriculum, or projects at school or college levels. This course is also approved for graduate credit.
Coming this fall the University of Vermont will be offering a bioenergy course taught by Anju Dahiya, cofounder of General Systems Research, LLC, lead biofuels instructor at the University of Vermont’s Rubenstein School of Environment and Natural Resources, and Vermont Bioenergy algae for biofuel grant recipient. This course is open to both degree and non-degree students from any background or department, as well as farmers, entrepreneurs, and teachers interested in developing curriculum, or projects at school or college levels. This course is also approved for graduate credit.
Potential participants are offered the option of variable credits, ranging from 0 to 6 credit hours. This allows prospective students to only attend lectures and have access to online course materials for 2 credits; further their experience with the addition of hands-on labs and field trips for 3 credits; or participate in all aspects of the class while additionally applying lessons to a service learning project with a community partner, earning 4 credits. Participants have the ability to add up to 2 more credits, totaling no more than 6, for additional work with the community partner pending special permission from the course instructor.
 Lectures will be held twice a week between September 18th and December 9th of 2015. Friday lectures will be on campus from 4:05 pm to 7:05 pm, followed by Saturday morning field trips between 10:00 am and 1:00 pm for those students who elected for 3 credits or more. The course required textbook, Bioenergy: Biomass to Biofuels, was edited by Anju Dahiya less than a year ago and represents a compilation of work from an extensive list of well-respected university extension programs, such as The University of Vermont Research Extension, as well as numerous national organizations including the US Department of Energy’s National Renewable Energy Laboratories.
Lectures will be held twice a week between September 18th and December 9th of 2015. Friday lectures will be on campus from 4:05 pm to 7:05 pm, followed by Saturday morning field trips between 10:00 am and 1:00 pm for those students who elected for 3 credits or more. The course required textbook, Bioenergy: Biomass to Biofuels, was edited by Anju Dahiya less than a year ago and represents a compilation of work from an extensive list of well-respected university extension programs, such as The University of Vermont Research Extension, as well as numerous national organizations including the US Department of Energy’s National Renewable Energy Laboratories.
Learn more about this course at the University of Vermont Renewable BioEnergy page or email the lead instructor Anju Dahiya at adahiya@uvm.edu.
 The Biomass Energy Resource Center (BERC), a program of the Vermont Energy Investment Corporation (VEIC), has launched a re-tooled web-based database for tracking the advancement of modern wood heating throughout North America. The newly revised searchable database houses key information on existing community-scale modern wood heating and combined heat and power systems across the U.S. and Canada, as well as an archive of links to case studies. Examples of community-scale facilities include schools, campuses, hospitals, prisons, multi-family or senior housing, government buildings, commercial buildings, and farms and greenhouses.
The Biomass Energy Resource Center (BERC), a program of the Vermont Energy Investment Corporation (VEIC), has launched a re-tooled web-based database for tracking the advancement of modern wood heating throughout North America. The newly revised searchable database houses key information on existing community-scale modern wood heating and combined heat and power systems across the U.S. and Canada, as well as an archive of links to case studies. Examples of community-scale facilities include schools, campuses, hospitals, prisons, multi-family or senior housing, government buildings, commercial buildings, and farms and greenhouses.
The database was originally created with funding from the U.S. Endowment for Forestry and Communities and further improvements were made with funding from the U.S. Department of Energy through the support of Vermont Senator Patrick Leahy. The re-tooled database is a user-friendly, interactive tool that will help collect and track information on a continuing basis. “This resource will provide stakeholders from a variety of backgrounds with a better understanding of the current demand for wood fuels as an energy source and the success of modern wood heating projects throughout North America,” said Adam Sherman, Manager of BERC at VEIC.
The database already contains more than 500 entries, but to ensure that this publicly available resource is accurate and up to date, BERC is asking for user participation. “We are committed to maintaining and building this database over time to ensure it remains a useful and reliable too, but this is a rapidly growing sector, so we need users to help,” said Sherman. “We need people to engage with the database; add new entries for facilities that have been missed and as new facilities come online, and edit existing entries that are incomplete.” With regular contributions, the database will continue to improve and grow.
With tens of thousands of annual visits and top Google search ranking, the BERC website is a high-visibility home for this important tool. The BERC database is designed to provide vital information on a specific subset of biomass energy facilities; community-scale biomass heating projects. The BERC database complements the Wood2Energy.org database that covers a broader spectrum of biomass energy facilities including power plants, sawmills, and pellet mills. Not only will the BERC database provide wood heating systems vendors the exposure and recognition for their projects, it also helps demonstrate that modern wood heating is becoming mainstream throughout North America. To learn more about using and contributing to the database visit www.biomasscenter.org/database.
About BERC
The Biomass Energy Resource Center (BERC) is a program of Vermont Energy Investment Corporation (VEIC). BERC works to advance the use of community-scale biomass energy throughout North America and beyond by providing technical consulting services, biomass energy program design and delivery, and education and outreach on benefits and best practices. BERC works with communities, federal, state and local governments, colleges and universities, businesses, utilities, and others to use local biomass resources, invest in local energy systems, and reduce the use of fossil heating fuels.
20 Apr 2015
Getting Smart About Vermont Energy
 The State of Vermont 2011 Comprehensive Energy Plan calls for 90% of Vermont energy needs to be met through efficiency and renewable sources by 2050. As Vermont residents witness continued high numbers in clean energy jobs, and advanced renewable energy legislation they will also need to take responsibility for Vermont to meet these goals, as every Vermonter will need to contribute in some way for Vermont to meet this ambitious goal. Enter Brighter Vermont, an action oriented program of the Energy Action Network, to help everyday Vermonters rethink where their energy comes from, how they use it in their daily lives, and what they can do to help the state reach its 90% by 2050 goal.
The State of Vermont 2011 Comprehensive Energy Plan calls for 90% of Vermont energy needs to be met through efficiency and renewable sources by 2050. As Vermont residents witness continued high numbers in clean energy jobs, and advanced renewable energy legislation they will also need to take responsibility for Vermont to meet these goals, as every Vermonter will need to contribute in some way for Vermont to meet this ambitious goal. Enter Brighter Vermont, an action oriented program of the Energy Action Network, to help everyday Vermonters rethink where their energy comes from, how they use it in their daily lives, and what they can do to help the state reach its 90% by 2050 goal.
The Brighter Vermont website is packed with testimonials and videos shared by individuals who describe the financial decisions they are making to positively affect the environment, Vermont’s economy, and their wallets. A family in Rutland reports on small home improvement they have made to keep out the Northeast cold out and share a video about lowering energy costs, with the help of Green Mountain Power, by properly weatherizing their home, changing to energy efficient LED bulbs, electing for a heat pump, and adding solar panels. The overall transition has made them a more energy conscious family and was achievable with a ten year loan the family is pleased to see being offset by reduction in energy costs.
A family in Burlington’s journey towards reducing their carbon footprint is documented in a fun testimonial video where the family picks out their first electric vehicle. They were able to replace one of their family vehicles with a zero emission Nissan Leaf (hyperlink to video) that was available with an affordable two year lease. The switch from a classic Vermont staple vehicle, a Subaru, to the Leaf, has helped the family not only save money at the gas pump, but the, as the family reports, electricity used to charge the vehicle comes from renewable energy. They enjoy educating their friends and neighbors about this carbon footprint transition.
Brighter Vermont also hosts ways for businesses, schools, and towns to become more efficient and promote renewables in their community. Methods for how schools and businesses have become more efficient by transitioning to modern wood heating. A featured video produced by VEIC (hyperlink) features 54 schools from across Vermont currently heating with wood chips and pellets which provides heat for nearly one third of k-12 students across Vermont. Our own Vermont Bioenergy Initiative Vermont on-farm energy videos are also featured for farmers to learn more about the emerging areas of oilseed, grass, and algae biofuel.
There is much that needs to be done in the fight against climate change and moving Vermont away from its reliance on fossil fuels. While this road can be daunting, it is important to remember that we can all make small changes that will benefit us, our community, and our state. And the Brighter Vermont website provides a fun and interactive platform for individuals, families, businesses, and institutions to learn how to contribute and share these efforts with others so Vermont can take steps towards meeting our renewable energy goals for our future.
Burlington, VT, March 16, 2015– Vermont Businesses for Social Responsibility (VBSR)
announced that it secured funding to continue the Business Energy Action (BEA) program through 2015. BEA works with companies to help them implement energy efficiency strategies that help to save 5% per year.
This additional funding for BEA is provided by the Vermont Bioenergy Initiative, a program of the Vermont Sustainable Jobs Fund. The Vermont Bioenergy Initiative connects diversified agriculture and local renewable energy production for on-farm and community use by supporting research, technical assistance, and infrastructure development in emerging areas of bioenergy, and overall education on the benefits of renewable energy and energy efficiency. Funding was made possible by the Office of US Senator Patrick Leahy and the US Department of Energy.
“We’re grateful for the support of Vermont Sustainable Jobs Fund as we work to help Vermont businesses reduce their need for fossil fuel,” said Andrea Cohen, Executive Director of Vermont Businesses for Social Responsibility. “Business Energy Action helps businesses be not only more responsible consumers of energy, but also helps their bottom line to create a more vibrant economy here in Vermont.”
Business Energy Action is currently working with more than 80 member businesses across the state.
About VBSR
Founded in 1990, VBSR is a statewide, non-profit business association with a mission to advance business ethics that value multiple bottom lines: economic, social, and environmental. Through education, public influence, and workplace quality, VBSR strives to help 760+ members set a high standard for protecting the natural, human, and economic environments of the state’s residents, while remaining profitable. Learn more or join the cause at www.vbsr.org.

Nick Meyer of North Hardwick Dairy, an Organic Valley milk producer, was able to reduce energy costs and increase self-sufficiency by growing sunflowers for biodiesel and meal while maintaining a wind turbine to help cover electricity needs.
We all know food gives us energy. But we might sometimes lose sight of the amount of energy involved in producing, processing and delivering that food to our plates. Everything requires energy: from tractors plowing and planting to producing fertilizer or compost; from milking cows and keeping that milk cold to storing and transporting vegetables. This energy costs farms real money and it is sometimes a major category of expense. Energy costs are typically one of the highest for farms, rivaling feed costs on dairy farms and labor costs on vegetable farms.
As Vermont experiences growth in food-related businesses and jobs, decisions about energy become more and more important. This has been part of Vermont’s Farm to Plate Strategic Plan and the associated network of people working on implementing that plan. The plan includes goals related to energy, including; reducing farm production expenses, reducing adverse environmental impacts from farm and food system activities, reducing energy use, and increasing renewable energy use in the food system.
One example of how this is actually working is a group called the Farm to Plate Energy Cross Cutting Team: a group of energy specialists from Efficiency Vermont, the Agency of Agriculture, UVM’s Rubenstein School and UVM Extension, The Vermont Bioenergy Initiative, USDA NRCS and private companies. The team meets regularly to learn from each other and take on specific projects such as the recent set of seven “Energy Success Stories” which were released at the 2014 Farm Show, showcasing farms, businesses, vendors, installers, and technical assistance providers who have made a difference with energy efficiency savings and renewable energy production.
Chaired by Efficiency Vermont planning manager, JJ Vandette, the energy team will continue to address the Farm to Plate Efficiency and Renewable Energy Goal to decrease overall food system energy consumption and increase food system renewable energy production and the Farm to Plate Environmental Impacts Goal to decrease adverse environmental impacts from farming and food system activities—while helping to decrease production expenses—also a goal of the Farm to Plate Strategic Plan.
The team is always interested in having new members. If you have an interest in energy, especially energy on farms and in the food system, we’d love to hear from you. JJ Vandette can be reached at jvandette@veic.org or 802.540.7915.
Data sources and analysis at www.vtfarmtoplate.com/getting-to-2020.
16 Feb 2015
Upcoming Farm Energy IQ Training
It’s not too late to register for the upcoming Farm Energy IQ Training for New England Agricultural Service Providers. This training will take place starting Monday, February 23rd at 8:00 a.m. and will end Wednesday February 25 in Fairlee, Vermont. Organized by individuals from the University of Vermont Extension Service, Penn State, and Rutgers University, this three day training is a great opportunity for those interested in on farm energy to learn and apply their skills as well as network with other attendees. The Farm IQ Energy Training is funded generously by Northeast Sustainable Agriculture Research and Education (SARE) Program as part of a regional professional development program to bring the latest developments in the field to individuals who can best apply them.
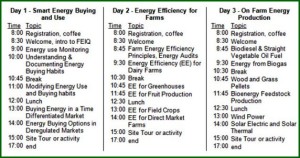
This conference will provide a range of opportunities to learn or improve energy purchasing, calculating, conservation, production, and analysis.Attendees will even have the opportunity to apply skills via hands-on activities and by visiting local operations. Over the three days these lessons will be compared for application on farms in different settings. In addition, attendees will receive a comprehensive binder with all the material covered in the workshops as well as supplemental materials to refresh and share material as well as continue learning.
This conference is a great opportunity to solidify one’s knowledge by learning from on hand specialist and being immersed with in the material. If you happen to miss this particular training, the same workshop will be offered in Pennsylvania, March 10th to the 12th and again in New Jersey from April 8th to the 10th.
Read more about renewable energy events around the country on the Vermont Bioenergy Field Notes blog
08 May 2014
Vermont Bioenergy Initiative releases report on grass heating energy potential in Vermont and the Northeast
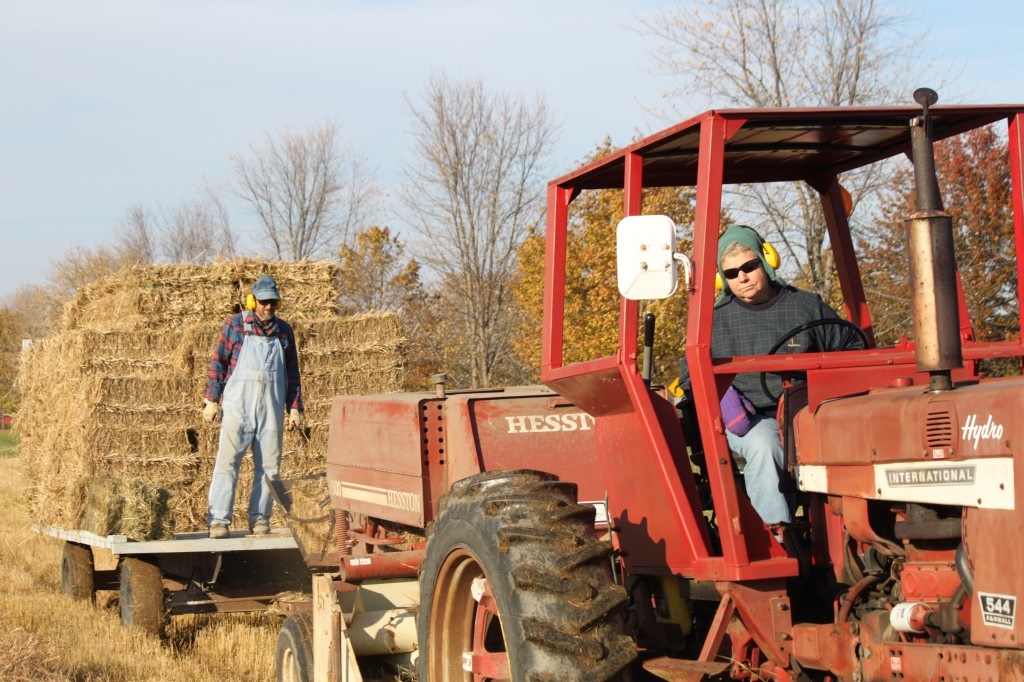

Baling switchgrass at Meach Cove Farm in Shelburne, Vermont. Photo Credit Vermont Bioenergy Initiative
Montpelier, VT – A new report evaluating grass biomass energy as a potential heating fuel has been released. Grass Energy in Vermont and the Northeast summarizes current research on the agronomy and usage potential of grass as a biofuel, and points to next steps for the region to fully commercialize this opportunity. The report was released last week by the Vermont Bioenergy Initiative, a program of the Vermont Sustainable Jobs Fund. The full report can be found on the Vermont Bioenergy Initiative website.
“There have been several independent assessments over the years of the various aspects of growing and burning grass for energy, but we were missing the step of linking it all together. We needed to put into one place what is currently known about grass energy, and get our remaining questions on paper,” says Sarah Galbraith, program manager of the Vermont Bioenergy Initiative. “It is very possible that grass as a heating fuel could enter into Vermont’s growing suite of renewable energy options. There are still uncertainties, but this report provides a series of recommendations and next steps for Vermont and the Northeast.”
The assessment for the report was conducted by members from Wilson Engineering Services and Ernst Conservation Seeds, and a former staff of Pennsylvania State University Cooperative Extension, who together conducted a literature review and interviews with experts in the field. The report was reviewed by the Vermont Agency of Agriculture, Food and Markets, University of Vermont Extension, Biomass Energy Resource Center, and the Vermont Sustainable Jobs Fund.

Grass for biofuels grow at the UVM Hort Farm in South Burlingon, Vermont. Photo credit Vermont Bioenergy Initiative
Grass Energy in Vermont and the Northeast includes key recommendations on models of grass energy that will work best for Vermont. Regional and closed loop processing were two models recommended, both involving farmers growing and harvesting grass, but differing in where the grass is processed into fuel and where it is used. The regional processing model calls for aggregating grass from a 50-mile radius at a central processing facility, where the grass is made into and used as fuel, or sold to local users. The closed loop model suggests farmers growing and processing grass on-site for on-farm or community use. Other models, like mobile on-farm processing and processing fuel for the consumer pellet market have significant hurdles to overcome if they are to be successful in Vermont.
Despite hurdles in some of the models presented, the report points to grass energy being a good option overall. “Native, warm-season grasses grown as a heating fuel are a viable energy crop for Vermont farmers wishing to diversify. Once the grasses are well-established, the input costs are minimal—especially compared to corn,” states Alexander DePillis, senior agriculture development coordinator for Vermont’s Agency of Agriculture, Food and Markets, an instrumental partner throughout planning for and publishing the grass energy report. “Grass thermal energy has the potential to help cut Vermont’s overall fuel bills while helping us meet the overall goal of the Comprehensive Energy Plan—for Vermont to obtain 90% of its energy from renewable sources by 2050.”
Perennial grasses can be grown on marginal lands not well suited for continuous row crop production and in open rural land currently not in agricultural production. The grass energy benefits reviewed in the report include retaining energy dollars in the local community, reducing greenhouse gas emissions from heating systems, improving energy security, providing a use for marginal farmland, and reducing pollution in soil and run-off from farms. Recommendations include a concerted effort in Vermont to plant grasses for energy on extended buffer strips along Lake Champlain, thereby reducing its nutrient load. Grass is a perennial crop harvested annually that can help level the increasing demand for forest biomass, while adding water quality and wildlife benefits by controlling erosion, reducing fertilizer use and providing cover and food for migrating and nesting birds.
In 2008, the Vermont Bioenergy Initiative began to explore the potential for grasses grown in Vermont to meet a portion of the state’s heating demand and reduce the consumption of non-renewable fossil fuels. The Grass Energy in Vermont and the Northeast report was initiated by the Vermont Sustainable Jobs Fund to aid in strategic planning for future grass energy program directives. The Vermont Bioenergy Initiative and subsequent grass energy report are funded by appropriations from the US Department of Energy secured by the Office of Senator Patrick Leahy.
The Vermont Bioenergy Initiative (www.vermontbioenergy.com) draws the connection between diversified agriculture and local renewable energy production for on-farm and community use. Aiming to supply farm inputs and reduce fossil fuel consumption, this program supports research, technical assistance, and infrastructure development in emerging areas of bioenergy. Since 2003 the program has focused on biodiesel production and distribution for heating and transportation, oil crops for on-farm biodiesel and feed, grass for heating, and algae production for biofuels and wastewater management. The Vermont Bioenergy Initiative is a program of The Vermont Sustainable Jobs Fund, a non-profit organization which provides financing, technical assistance and other resources to Vermont businesses who develop products and services and create jobs in the fields of renewable energy, and sustainable agriculture and forestry.
17 Jan 2014
Vermont Bioenergy Initiative: Video