19 Oct 2015
Field to Flue Open House at Meach Cove Farms

Vermont-grown grasses are being used to heat the Biomass Building – a 4,200 square foot commercial building at Meach Cove Farms in Shelburne. Local residents, community leaders, and renewable energy enthusiasts are invited to visit Meach Cove Farms Friday, October 23 – Saturday, October 24 for an Open House to learn how grass pellets are generating heat in a biomass boiler – an emerging source of bioenergy in Vermont.
Meach Cove Farms is a 1,000-acre certified organic farm primarily growing soy beans, wheat, rye, and corn as well as wine grapes, woodlands, and switchgrass trial plots for use in grass energy production. The Open House will offer a complete demonstration of the Grass Pellet Heating Equipment Combustion Optimization project – the first project in New England to showcase grass test plots, densification equipment, and an EvoWorld biomass boiler that burns the grass.
Meach Cove Farms began collaborating with Dr. Sidney Bosworth of the University of Vermont College of Agriculture and Life Sciences and the Vermont Bioenergy Initiative in 2009 to assess the potential of different species of grass as solid biofuel for heating applications.
In September 2011 Meach Cove Farms was awarded an USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service Conservation Innovation Grant to research the feasibility of Vermont grown grass pellets and heating equipment potential as an emerging renewable energy source in Vermont. The biomass boiler being featured at the Open House was funded through a Conservation Innovation Grant (CIG) administered by the Natural Resources Conservation Services.
IF YOU GO:
Meach Cove Farms is located at 310 Beach Road in Shelburne (off Bostwick Road, 1.6 miles west of Rte 7). The Open House runs from 9 am – 12 noon both Friday and Saturday, October 23-24. There is no cost and both days are open to the public. More info at www.meachcovefarms.org, 802-985-9218.
14 Sep 2015
Vermont Farmer Helps Others Produce Biofuel
 The Vermont Bioenergy Initiative, a program of the Vermont Sustainable Jobs Fund, aims to foster the sustainable bioenergy through a local production for local use model, proven to work for Vermont. Since 2003 the program has allowed Vermont farms to ease their resilience on inconsistently priced, foreign fossil fuels and other agricultural inputs. This is accomplished by focusing on biodiesel production and distribution for heating and transportation, oil crops for on-farm biodiesel and feed, grass energy for heating, and algae production for biofuels and waste management.
The Vermont Bioenergy Initiative, a program of the Vermont Sustainable Jobs Fund, aims to foster the sustainable bioenergy through a local production for local use model, proven to work for Vermont. Since 2003 the program has allowed Vermont farms to ease their resilience on inconsistently priced, foreign fossil fuels and other agricultural inputs. This is accomplished by focusing on biodiesel production and distribution for heating and transportation, oil crops for on-farm biodiesel and feed, grass energy for heating, and algae production for biofuels and waste management.
Vermont Bioenergy Initiative grantees have shown just how much the addition of biomass feedstock can contribute to sustainable agriculture. As one of these grantees, John Williamson of Stateline Farm would put it, “100 years ago everyone produced their own fuel; we are just doing that now in a different way.” This is really a novel way to look of what he is doing on his North Bennington farm. John was featured in a recent story in Daily Yonder which outlined his work and how he has begun helping his Vermont neighbors find their path to this form of sustainable, renewable energy.
For more about John Williamson’s on-farm biodiesel production, watch this video of John in self-designed Biobarn. He and Chris Callahan of University of Vermont Extension show us how they can grow oil crops, make biodiesel, feed animals, and save money!
Also, explore the initiative’s extensive and accessible set of bioenergy resources for replication in rural communities across the United States and beyond.
The Vermont Bioenergy Initiative connects diversified agriculture and local renewable energy production for on-farm and community use by supporting research, technical assistance, and infrastructure development in emerging areas of bioenergy including biodiesel production and distribution for heating and transportation, oil crops for on-farm biodiesel and feed, grass for heating, and algae production for biofuels and wastewater management. Explore the initiative’s extensive and accessible set of bioenergy resources for replication in rural communities across the United States and beyond.
Video
A series of informative educational showcase a range of biofuel possibilities; from research and crop farming to feedstocks and fuel. The videos were developed by the Vermont Sustainable Jobs Fund, UVM Extension researchers, KSE Partners, and the Vermont Bioenergy Initiative grantees.
Calculators
Two calculators, developed by UVM Extension, help connect potential costs and profits associated with oilseed production:
- Grass Biomass Production and Harvest Cost Estimator
- Vermont Oilseed Crop Production Cost and Profit Calculator
Course Work
- Biomass to Biofuels, University of Vermont: This semester-long course covers liquid and solid biofuels, biogas and bio-electricity, and environmental, social and economic issue related to biofuels. The course includes guest lecturers and field days. Available for variable credits.
- Biomass to Biofuels, Vermont Technical College: The development of this course and associated materials led to an online repository of resources for the classroom covering biomass to biofuels.
- Digester Operations Master Certificate, Vermont Technical College: a twelve week program designed for participants to work directly with operations staff of Vermont Tech’s anaerobic digester and come away with understanding of the mechanics and operations of a digester system, as well as other areas such as permitting, regulatory compliance and record keeping.
- Alternative Fuel Vehicles: Biodiesel, part of the Green Trainings series at Vermont Technical College: This 2-day course covers engine systems, biodiesel blends and biodiesel production, including a demonstration of fuel-making equipment.
- Biofuels Course at Yestermorrow Design/Build School, part of the Green Trainings series at Vermont Technical College: This weekend workshop enables students to begin replacing fossil fuels with biofuels, such as adapting engines to run on straight vegetable oil. 1 credit.
Textbook
Bioenergy: Biomass to Biofuels; is an innovative new textbook that provides insight into the potential and current advances and benefits of biofuel. Contributions include an extensive list of well-respected university extension programs, such as The University of Vermont Research Extension, as well as numerous national organizations including the US Department of Energy’s National Renewable Energy Laboratories.
Reports
A variety of reports are available which cover a range of topics including seed preparation and storage:
- Institute for Energy and the Environment at Vermont Law School.Legal & Regulatory Review of On-farm Biodiesel Production. 2015.
- Chris Callahan and Netaka White,Vermont On-Farm Oilseed Enterprises: Production Capacity and Break-even Economics. July 2013.
- Nell Campbell, Local Production for Local Use to Supply a Portion of Vermont’s Energy Needs.May 2009.
- Emily J. Stebbins. Technical and Economic Feasibility of Biodiesel Production in Vermont: Evidence From a Farm-Scale Study and a Commercial-Scale Simulation Analysis. May 2009.
- Christopher W. Callahan,A Feasibility Analysis of a Mobile Unit for Processing Oilseed Crops and Producing Biodiesel in Vermont. December 2008.
- Emily Stebbins, The Market Potential of Farm-Scale Oilseed Crop Products in Vermont. February 2008. (See also the Executive Summary)
- John Williamson & Tanner Williamson – State Line Biofuels, LLP, Chris Callahan – Callahan Engineering, PLLC, Feasibility Analysis:_Solar Seed Dryer and Storage Bin at State Line Farm, Bennington, VT. October 2008
- Christopher W. Callahan, A Feasibility Study of a Mobile Unit for Processing Oilseed Crops and Producing Biodiesel in Vermont. December 2008
- Kenneth Mulder, Ph.D., Galen Wilkerson, Emily J. Stebbins.Homegrown Fuel: Economic Feasibility of Commercial-Scale Biodiesel Production in Vermont. September 2007.
- The Vermont Biodiesel Project: Building Demand in the Biofuels Sector – Final Report. October 2006. (See also theExecutive Summary)
- Vermont Department of Buildings and General Services, Vermont Biodiesel Pilot Project: Emissions Testing of Biodiesel Blends With #6 Fuel Oil At the Waterbury State Office Complex – Final Report. September 2006.
- Laboratory and Field Testing of Biodiesel in Residential Space Heating Equipment – Final Report. August 2006.
- Vermont Biodiesel Supply Chain Survey – Final Report. April 2006.
- Wilson Engineering,Grass Energy in Vermont and the Northeast, May 2014.
Technical Advice
Connect directly with the Vermont Bioenergy Initiative’s technical assistance providers:
Oilseeds for Biofuel
- Heather Darby, Agronomic and Soils Specialist
- University of Vermont Extension, Northwest Crops and Soils Team
- (802) 524-6501
- darby@uvm.edu
- Chris Callahan, PE, Agricultural Engineer
- University of Vermont Extension
- (802) 773-3349
- callahan@uvm.edu
Grass for Heating Fuel
- Sidney Bosworth, Extension Professor
- University of Vermont College of Agriculture and Life Sciences
- (802) 656-0478
- bosworth@uvm.edu
Algae for Biodiesel
- Anju Dahiya, Instructor and Principal
- University of Vermont and GSR Solutions
- (802) 310-1936
- adahiya@uvm.edu
17 Aug 2015
The Third Annual National Bioenergy Day
The T hird Annual National Bioenergy Day (NBD), which will take place Wednesday, October 21st, is a day that is marked with events from across the country that celebrates energy independence, local jobs, and many other benefits of local bioenergy. Led by Biomass Power Association in partnership with U.S. Forest Service, National Bioenergy Day is an opportunity for Vermonters to showcase our research, progress, and impacts in producing local bioenergy for local use.
hird Annual National Bioenergy Day (NBD), which will take place Wednesday, October 21st, is a day that is marked with events from across the country that celebrates energy independence, local jobs, and many other benefits of local bioenergy. Led by Biomass Power Association in partnership with U.S. Forest Service, National Bioenergy Day is an opportunity for Vermonters to showcase our research, progress, and impacts in producing local bioenergy for local use.
How To Get Involved:
- Organize an event on or near October 21ndthat showcases bioenergy as a clean, efficient, and resourceful way to produce energy. Emphasizes bioenergy’s role in improving environmental health; and facilitates collaboration along the supply chain.
- Partner with someone who works in the bioenergy supply chain to create an event. Use the Vermont Energy Atlas to find partners in your area.
- Piggyback on an existing event and call it a NBD event.
- Share and talk about NBD in your social media and press efforts while promoting impacts in your community.
The Vermont Bioenergy Initiative, for example, will spend the day re-capping and previewing events and research on our Twitter handle @VTBioenergy that took place throughout the summer and that are planned for the fall. We’ll be recapping and sharing exciting things like the exciting learning opportunities at the University of Vermont, Full Sun Company’s Biodiesel and Meal production, and much more!
For more information, you can visit also visit bioenergyday.com and follow @USAbiomass on twitter!
Click Here for National Bioenergy Day Participation Guide!
27 Jul 2015
Summit on Creating Prosperity and Opportunity Confronting Climate Change – Looking Back and Looking Forward
 The Summit on Creating Prosperity and Opportunity Confronting Climate Change brought together over 400 innovative business, non‐profit, and community leaders, elected officials, public policy advocates, students, and interested residents to begin to frame policy and investment strategies to advance the development of the Vermont Climate Economy. Summit participants developed a list of key practical actions to serve as a launching point for the Vermont Climate Change Economy Council (VCCEC), a group charged with a one year mission to develop a structured plan with practical actions to reduce carbon emissions and stimulate green economic development in Vermont. The Council will build a set of public/private strategies designed to promote economic opportunity, innovative business development, investment, and job creation in Vermont.
The Summit on Creating Prosperity and Opportunity Confronting Climate Change brought together over 400 innovative business, non‐profit, and community leaders, elected officials, public policy advocates, students, and interested residents to begin to frame policy and investment strategies to advance the development of the Vermont Climate Economy. Summit participants developed a list of key practical actions to serve as a launching point for the Vermont Climate Change Economy Council (VCCEC), a group charged with a one year mission to develop a structured plan with practical actions to reduce carbon emissions and stimulate green economic development in Vermont. The Council will build a set of public/private strategies designed to promote economic opportunity, innovative business development, investment, and job creation in Vermont.
Over the course of 2015, VCCEC will evaluate findings, key ideas and suggested action steps derived from the Summit, lead regional public forums, evaluate and summarize research findings, interview key stakeholder groups, and consider model economic development strategies from other state and countries. During 2015, the group will develop a strategic platform of recommendations for action, and report to the Vermont legislature, the Governor of Vermont and the public in January 2016. The Vermont Council on Rural Development (VCRD) will provide support to their work and then help promote the platform of action that comes from its deliberants. Goals of the Vermont Climate Change Economy Council are to:
- Identify opportunities created by climate change to strengthen Vermont’s economy through strategies advancing key business clusters and economic sectors.
- Build an increased sense of unity in Vermont around policies to confront and mitigate the impact of climate change and to advance economic opportunities and solutions that respond to climate change.
- Build a public information campaign to celebrate innovation and Vermont’s green business leadership; internally and externally marketing to build the Vermont brand as an economic/environmental problem solver.
- Expand Vermont’s economic brand around climate change solutions to retain and attract youth and creative entrepreneurs to locate throughout the state.
Vermont businesses and nonprofits are addressing climate change – both its challenges and opportunities. Their creative solutions are a growing part of our state’s economy. What are your experiences? Do you have ideas about how Vermont can grow jobs and nurture innovative business development in sectors ranging from clean energy, to recycling, transportation systems, and thermal efficiency?
Jo![Regional_Forum_Flyer5_15_statewide[1]](http://vermontbioenergy.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/Regional_Forum_Flyer5_15_statewide1-150x150.jpg) in the Vermont Council on Rural Development and local business leaders at a forum on “What’s Next for Vermont’s Climate Change Economy?” Forums will take place at 7:00pm at the Paramount in Rutland (Aug 26), the Latchis Hotel in Brattleboro (Oct 6), and City Hall in Burlington (Oct 29). Come to the forum(s) most convenient for you.
in the Vermont Council on Rural Development and local business leaders at a forum on “What’s Next for Vermont’s Climate Change Economy?” Forums will take place at 7:00pm at the Paramount in Rutland (Aug 26), the Latchis Hotel in Brattleboro (Oct 6), and City Hall in Burlington (Oct 29). Come to the forum(s) most convenient for you.
These forums are the next step for public input to the Vermont Climate Change Economy Council, a group working to develop a practical plan to reduce carbon emissions and stimulate economic development in Vermont. To learn more about the forums and the Council visit VCRD’s website at vtrural.org, download the event flyer (pdf).
For more information about the results of the summit, Click HERE to read the report and follow the hashtag #VTClimateEconomy and Vermont Council on Rural Development on Twitter at @VTRuralDev for more updates!
Farms open their doors to a public interested in learning more about where food comes from and supporting the local agricultural economy
Farmers across Vermont will throw open their barn doors and garden gates to welcome the public for a behind-the-scenes look at Vermont’s vibrant working landscape. Vermont’s first Open Farm Week will be held Monday, August 3 – Sunday, August 9, 2015.
Open Farm Week is a weeklong celebration of Vermont farms. Over 100 farms are participating, many of whom are not usually open to the public. Open Farm Week offers Vermonters and visitors alike educational opportunities to learn more about local food origins, authentic agritourism experiences, and the chance to build relationships with local farmers. Activities vary and may include milking cows and goats, harvesting vegetables, collecting eggs, tasting farm fresh food, scavenger hunts, hayrides, farm dinners, and live music.
Visit DigInVT for a map of participating farms by region. Many events are free and costs vary depending on what activities are offered. Everyone is invited to join the #VTOpenFarm conversations on social media. All participating farms, geographic location, and offerings are at www.DigInVT.com.
Farmers’ markets will also be a part of the Open Farm Week celebration as organizers planned the event to coincide with National Farmers’ Market Week – also the first week of August.
The first Vermont Buy Local Market on the Statehouse Lawn will be held during Open Farm Week on Tuesday, August 4th from 10am-1pm. The Vermont Agency of Agriculture, Food and Markets is organizing the first Statehouse farmers’ market in collaboration with the Capital City Farmers’ Market and NOFA-VT.
Building off of the success of NOFA-VT’s 2014 Open CSA Farm Day, Open Farm Week is a collaborative statewide agritourism project organized by members of the Vermont Farm to Plate Network including Intervale Center, Vermont Farm Tours, Neighboring Food Co-op Association, Vermont Agency of Agriculture, Vermont Fresh Network, Vermont Department of Tourism, Shelburne Farms and Farm-based Education, NOFA-VT, and City Market. Open Farm Week helps Vermont reach its statewide Farm to Plate food system plan goals to increase farm profitability, local food availability, and consumption of Vermont food products.
Vermont Open Farm Week is made possible by the generous support of Premiere Sponsor: City Market/Onion River Coop as well as the Vermont Department of Tourism and Marketing; Vermont Agency of Agriculture, Food and Markets, Localvore Today and Woodchuck Hard Cider.
Vermont’s solar industry is lauding Governor Peter Shumlin’s proclamation of the third Saturday in June as “Celebrate Solar Day” in Vermont.
The solar proclamation, announced at the Whitcomb Farm in Essex, coincides with this June 20th, when solar projects in communities throughout Vermont will be open for public tours. June 20 is the weekend of the Summer Solstice.
Like open sugarhouse weekend in the spring and open art studio weekend in the fall, the inaugural summertime tours will give Vermonters the opportunity to get an up-close view of solar systems to learn about the technology, solar economics, and the benefits of solar to our community. Solar customers, host farmers, and owners will be on-hand to speak with the public.
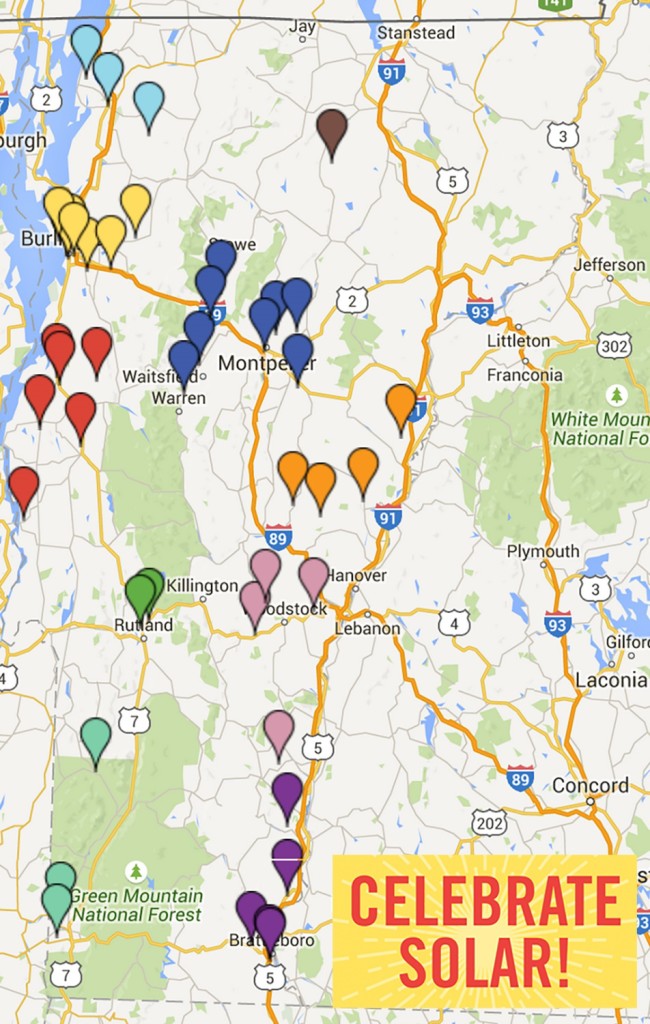
More than 50 systems across all regions of the state will be participating in Celebrate Solar Tours and a map of open tours can be found here. Many participating sites will host refreshments, music, or other entertainment. Other planned solar events include community walking tours of residential solar installations, miniature golf, a self-guided bike tour, and on-site yoga.
The Governor’s proclamation notes that “solar energy represented 99% of new electrical capacity in the state in 2014 and more than 5,000 Vermont customers have installed solar” through Vermont’s net metering program.
Further, it cites that the Vermont clean energy industries employ over 15,000 Vermonters, with solar providing “a broad spectrum of employment opportunities, helping retain and attract Vermonters working in manufacturing, installation, and sales, among other careers.”
The Whitcomb family is host to a 2.2 Megawatt solar farm that provides energy for Vermont’s SPEED program.
Among the solar sites open to tour June 20: iconic and sweet Vermont attractions like Cold Hollow Cider and Morse Farm Maple Sugarworks, high-tech attractions like Draker and Small Dog Electronics, agricultural farms like Champlain Orchards, shared community solar arrays, and some of Vermont’s highest producing solar farms.
At the announcement of the solar tours, Paul Brown, owner of Cold Hollow Cider in Waterbury Center, which has a 150kW system powering its operations, said of the event, “Folks know us and visit us for our cider and donuts. But we are thrilled to open up the field behind our cidery to share the benefits of solar technology to our business and our community. We’ll of course also be serving up some sweet treats for those who come by.”
About Celebrate Solar Tours – June 20
The first annual Celebrate Solar Tours on June 20 will feature public tours of more than 50 solar systems of varying size throughout the state. The public will have the opportunity to get an up-close understanding of the technology, economics and benefits to the community. Open systems will be designated with roadway signage and many will feature music, refreshments or other entertainment.
Contact: Ansley Bloomer
Ansley@revermont.org or 802-595-0723
08 Jun 2015
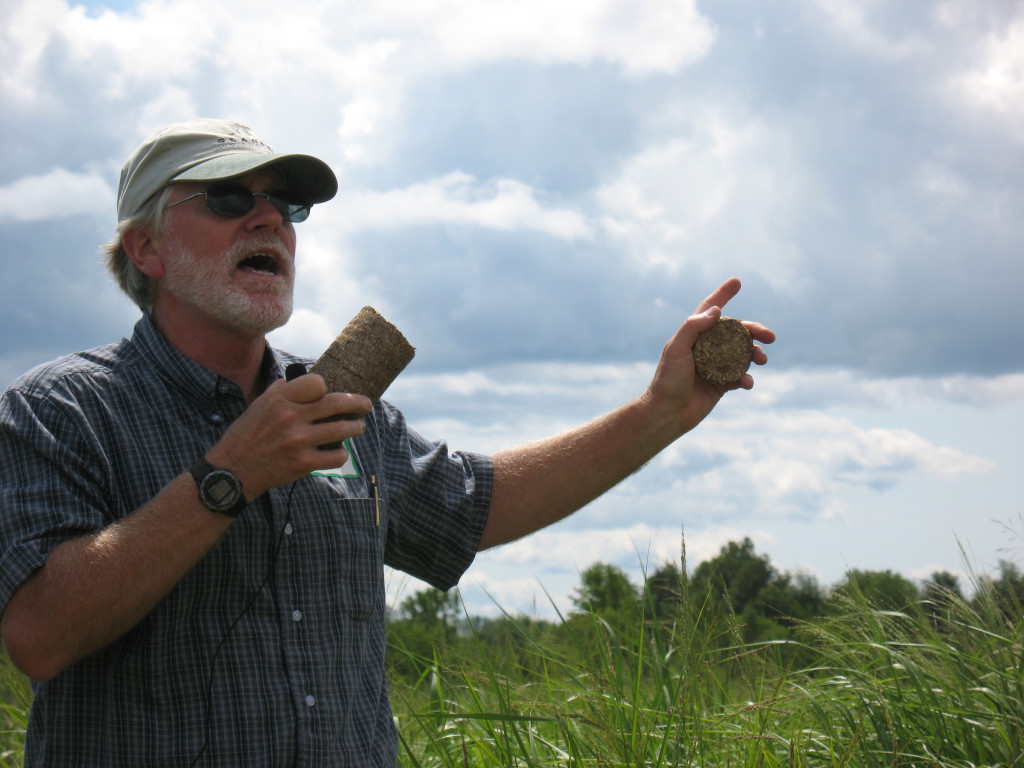
Grass Energy in Vermont

University of Vermont Extension Agronomist, Sid Bosworth explains in the field his research into use of grasses for combustion and thermal energy
In 2008, the Vermont Bioenergy Initiative began to explore the potential for grasses energy grown in Vermont to meet a portion of the state’s heating demand and reduce the consumption of non-renewable fossil fuels. The Grass Energy in Vermont and the Northeast report was initiated by the Vermont Sustainable Jobs Fund, and carried out by its program the Vermont Bioenergy Initiative, to aid in strategic planning for future grass energy program directives.
Grass Energy in Vermont and the Northeast summarizes current research on the agronomy and usage potential of grass as a biofuel, and points to next steps for the region to fully commercialize this opportunity. The keys to commercializing grass for energy are improving fuel supply with high-yielding crops, establishing best practices for production and use, developing appropriate, high-efficiency combustion technology, and building markets for grass fuel.
Perennial grasses, while serving as a biomass feedstock for heating fuel, also have numerous other benefits to farmers. The grass energy benefits reviewed in the report include retaining energy dollars in the local community, reducing greenhouse gas emissions from heating systems, improving energy security, providing a use for marginal farmland, and reducing pollution in soil and run-off from farms.
Regional and closed loop processing were two models recommended by the report, both involving farmers growing and harvesting grass, but differing in where the grass is processed into fuel and where it is used. The regional processing model calls for aggregating grass from a 50-mile radius at a central processing facility, where the grass is made into and used as fuel, or sold to local users. The closed loop model suggests farmers growing and processing grass on-site for on-farm or community use. Other models, like mobile on-farm processing and processing fuel for the consumer pellet market have significant hurdles to overcome if they are to be successful in Vermont.
In the below video a Vermont agronomist explains switchgrass production followed by entrepreneurs turning bales of grass into briquette fuel. This grass biofuel feedstock can be grown alongside food production on marginal agricultural lands and abandoned pastures, and in conserved open spaces. The harvested grass can be baled and used as-is in straw bale combustion systems, or it can be compressed into several useable forms for pellet fuel combustion systems.
For more information on grass biofuel feedstocks and to read the full Grass Energy in Vermont and the Northeast report visit the grass energy section of the Vermont Bioenergy website.
In order to meet the goals set by Vermont’s comprehensive energy plan for Vermont to produce 90 percent of the state’s energy needs from renewables by 2050 and reduce Vermont’s greenhouse gas emissions by 50 percent from a 1990 baseline, Vermont farmers will have an important role to play. As Vermont experiences growth in food-related businesses and jobs, decisions about energy become more important prompting statewide energy and agriculture collaborations. In the following episodes of Across the Fence, UVM Extension agricultural engineer and Vermont Bioenergy Initiative biofuels consultant, Chris Callahan, shares two stories about Vermont farmers who are rethinking their on-farm energy. In both examples UVM extension is able to work with the farmers to help make cleaner, renewable on-farm energy sources a practical solution that saves money and results in greenhouse gas reductions.
Learn more in a series of on-farm energy case studies produced by Vermont’s Farm to Plate Initiative.
 Coming this fall the University of Vermont will be offering a bioenergy course taught by Anju Dahiya, cofounder of General Systems Research, LLC, lead biofuels instructor at the University of Vermont’s Rubenstein School of Environment and Natural Resources, and Vermont Bioenergy algae for biofuel grant recipient. This course is open to both degree and non-degree students from any background or department, as well as farmers, entrepreneurs, and teachers interested in developing curriculum, or projects at school or college levels. This course is also approved for graduate credit.
Coming this fall the University of Vermont will be offering a bioenergy course taught by Anju Dahiya, cofounder of General Systems Research, LLC, lead biofuels instructor at the University of Vermont’s Rubenstein School of Environment and Natural Resources, and Vermont Bioenergy algae for biofuel grant recipient. This course is open to both degree and non-degree students from any background or department, as well as farmers, entrepreneurs, and teachers interested in developing curriculum, or projects at school or college levels. This course is also approved for graduate credit.
Potential participants are offered the option of variable credits, ranging from 0 to 6 credit hours. This allows prospective students to only attend lectures and have access to online course materials for 2 credits; further their experience with the addition of hands-on labs and field trips for 3 credits; or participate in all aspects of the class while additionally applying lessons to a service learning project with a community partner, earning 4 credits. Participants have the ability to add up to 2 more credits, totaling no more than 6, for additional work with the community partner pending special permission from the course instructor.
 Lectures will be held twice a week between September 18th and December 9th of 2015. Friday lectures will be on campus from 4:05 pm to 7:05 pm, followed by Saturday morning field trips between 10:00 am and 1:00 pm for those students who elected for 3 credits or more. The course required textbook, Bioenergy: Biomass to Biofuels, was edited by Anju Dahiya less than a year ago and represents a compilation of work from an extensive list of well-respected university extension programs, such as The University of Vermont Research Extension, as well as numerous national organizations including the US Department of Energy’s National Renewable Energy Laboratories.
Lectures will be held twice a week between September 18th and December 9th of 2015. Friday lectures will be on campus from 4:05 pm to 7:05 pm, followed by Saturday morning field trips between 10:00 am and 1:00 pm for those students who elected for 3 credits or more. The course required textbook, Bioenergy: Biomass to Biofuels, was edited by Anju Dahiya less than a year ago and represents a compilation of work from an extensive list of well-respected university extension programs, such as The University of Vermont Research Extension, as well as numerous national organizations including the US Department of Energy’s National Renewable Energy Laboratories.
Learn more about this course at the University of Vermont Renewable BioEnergy page or email the lead instructor Anju Dahiya at adahiya@uvm.edu.