02 Nov 2015
Vermont Bioenergy Initiative proves biofuel potential for state and concludes ten year project
By: Ellen Kahler

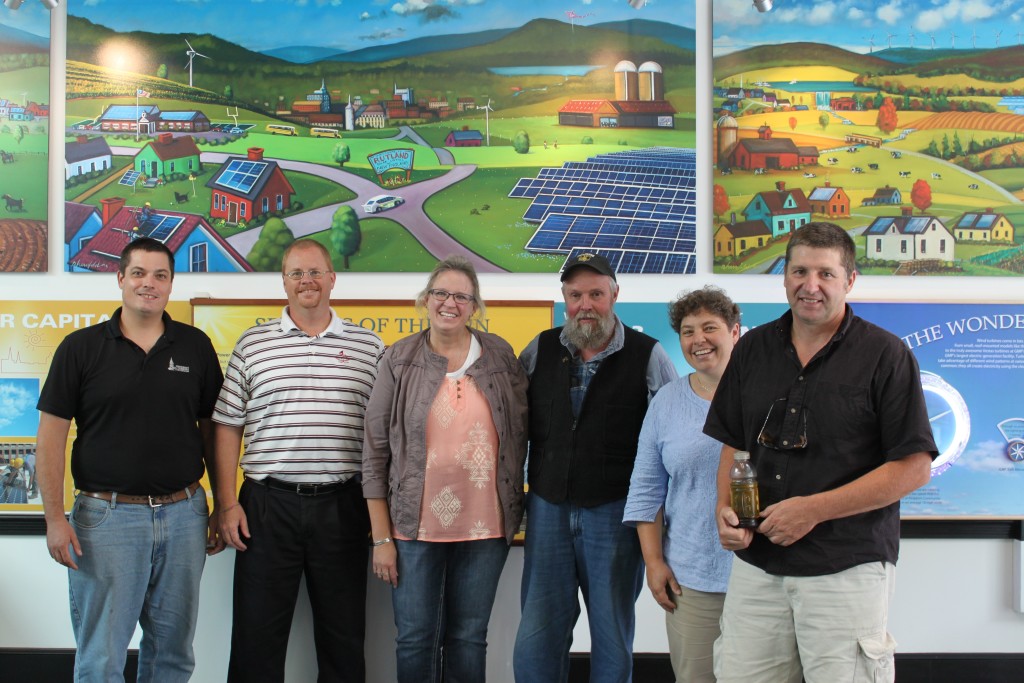
VT Bioenergy Team – L to R (Chris Callahan – UVM Extension, Kirk Shields — Green Mountain Power, Christy Sterner – US DOE, Larry Scott – Ekolott Farm, Ellen Kahler – VSJF, John Williamson – Stateline Biofuels) at Green Mountain Power’s Energy Innovation Center in Rutland
Vermont can produce more of its own biofuel energy and the environmental and potential economic benefits of local bioenergy have been proven by the Vermont Bioenergy Initiative – a program of the Vermont Sustainable Jobs Fund. Since 2005, the Vermont Bioenergy Initiative has invested more than $2.5 million in innovative bioenergy research, projects, and people so Vermont can locally produce more of the state’s energy needs – from a variety of agricultural and algal feedstocks.
US Senator Patrick Leahy made the investment at this scale possible through Congressionally Directed Awards from the US Department of Energy (US DOE). The funding concludes in early 2016, at which point a complete impact report will be released by the Vermont Sustainable Jobs Fund, who has served as the intermediary between the US DOE and 52 individual Vermont bioenergy projects over the past ten years.
Research, development, and early stage demonstration projects have included:
- Investing in 2 on-farm methane digesters;
- Building farm-scale infrastructure to turn oilseed crops such as sunflowers into biodiesel to run farm tractors;
- Growing switchgrass and densifying it into “pucks” that are burned in a high efficiency commercial boiler instead of propane;
- Identifying the most lipid producing strains of native Vermont algae which can feed off the excess nutrients from methane digesters and can eventually be harvested to make biodiesel or jet fuel;
- Developing two “Biomass to Biofuels” college level courses which run repeatedly at UVM and VT Tech to inspire and train the next generation of bioenergy experts and technicians;
- Exploring the logistics of bulk wood pellet delivery systems to Vermonters’ homes;
- Organizing a number of learning opportunities and conferences for oilseed, grass and algae researchers, farmers and entrepreneurs to attend;
- Providing agronomic and engineering support to oilseed and grass farmers;
- Educating the general public about why the local production for local use of energy crops from Vermont farms and forests makes good economic and ecological sense.

VT Bioenergy Team 2 – L to R (Roger Rainville – Borderview Farm, Christy Sterner – US DOE, Heather Darby – UVM Extension, Natasha Rainville – Borderview Farm) at Borderview Farm, Alburgh VT
The Vermont Bioenergy Initiative is a unique effort and one that is gaining resonance in other parts of rural America. The initiative’s resource website, www.VermontBioenergy.com is utilized by biofuel producers, educators, and technical service providers from across the country.
The work conducted over the past ten years by the Vermont Bioenergy Initiative to conduct research, provide technical assistance, and develop infrastructure in emerging areas of bioenergy will continue with the initiative’s partners at UVM Extension and the Vermont Agency of Agriculture, Food & Markets. As Vermont moves forward – being innovative and increasingly focused on generating renewable energy from the land and forests – the research and infrastructure the Vermont Bioenergy Initiative has invested in over the past ten years will endure and spawn the next wave of bioenergy development in the state.
Ellen Kahler is executive director of the Vermont Sustainable Jobs Fund (VSJF), a non-profit organization created by the State of Vermont to help develop Vermont’s sustainable agriculture, renewable energy, and forest product businesses. Since 2005, the Vermont Bioenergy Initiative has been a VSJF program that connects diversified agriculture and local renewable energy production for on-farm and community use by supporting research, technical assistance, and infrastructure development in emerging areas of bioenergy including biodiesel production and distribution for heating and transportation, oil crops for on-farm biodiesel and feed, grass for heating, and algae production for biofuels and wastewater management. Learn more at www.VermontBioenergy.com.
19 Oct 2015
Field to Flue Open House at Meach Cove Farms

Vermont-grown grasses are being used to heat the Biomass Building – a 4,200 square foot commercial building at Meach Cove Farms in Shelburne. Local residents, community leaders, and renewable energy enthusiasts are invited to visit Meach Cove Farms Friday, October 23 – Saturday, October 24 for an Open House to learn how grass pellets are generating heat in a biomass boiler – an emerging source of bioenergy in Vermont.
Meach Cove Farms is a 1,000-acre certified organic farm primarily growing soy beans, wheat, rye, and corn as well as wine grapes, woodlands, and switchgrass trial plots for use in grass energy production. The Open House will offer a complete demonstration of the Grass Pellet Heating Equipment Combustion Optimization project – the first project in New England to showcase grass test plots, densification equipment, and an EvoWorld biomass boiler that burns the grass.
Meach Cove Farms began collaborating with Dr. Sidney Bosworth of the University of Vermont College of Agriculture and Life Sciences and the Vermont Bioenergy Initiative in 2009 to assess the potential of different species of grass as solid biofuel for heating applications.
In September 2011 Meach Cove Farms was awarded an USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service Conservation Innovation Grant to research the feasibility of Vermont grown grass pellets and heating equipment potential as an emerging renewable energy source in Vermont. The biomass boiler being featured at the Open House was funded through a Conservation Innovation Grant (CIG) administered by the Natural Resources Conservation Services.
IF YOU GO:
Meach Cove Farms is located at 310 Beach Road in Shelburne (off Bostwick Road, 1.6 miles west of Rte 7). The Open House runs from 9 am – 12 noon both Friday and Saturday, October 23-24. There is no cost and both days are open to the public. More info at www.meachcovefarms.org, 802-985-9218.
![12038666_988361397888752_7565829410015974342_o[2]](http://vermontbioenergy.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/10/12038666_988361397888752_7565829410015974342_o2-1024x731.jpg) On October 6th, Seventh Generation and the University of Vermont welcomed the 45th US Vice President, Al Gore at Ira Allen Chapel on the university’s campus. The highly anticipated speaking engagement entitled “The Climate Crisis and the Case for Hope,” which is part of an Energy Action Seminar Series facilitated by UVM Energy Alternatives, was truly an emotional roller coaster and had Gore left the stage at the halfway mark, all in attendance would have gone home rather depressed. “We are going to win this struggle” he stated, “the question is how quickly we will win,” Gore remarked before elaborating on the deep sinkhole humanity has fallen into.
On October 6th, Seventh Generation and the University of Vermont welcomed the 45th US Vice President, Al Gore at Ira Allen Chapel on the university’s campus. The highly anticipated speaking engagement entitled “The Climate Crisis and the Case for Hope,” which is part of an Energy Action Seminar Series facilitated by UVM Energy Alternatives, was truly an emotional roller coaster and had Gore left the stage at the halfway mark, all in attendance would have gone home rather depressed. “We are going to win this struggle” he stated, “the question is how quickly we will win,” Gore remarked before elaborating on the deep sinkhole humanity has fallen into.
The lecture followed a path most familiar with the former vice president’s advocacy would expect. The rising atmospheric greenhouse gas (GHG) levels that we are witnessing come from a variety of sources, but as Gore pointed out “the main problem is burning of fossil fuels, when we address this, the rest will fall into place.” The first part of the lecture really focused on the crisis. The audience watched in horror footage of major weather events, many have seen before, but taken in all at once really underline the major recent changes that we have seen in our global weather patterns. Gore noted that of the “14 of the hottest years on record have been in the last 15 years,” and that the average temperature at night during this time has increased, meaning that people and the planet, really can’t get a break from the heat.
Gore went on to talk about the cost of carbon, or as he tried to drive home, the lack of cost it represents to our economy. “We need to put a cost on carbon,” he noted “put a cost on denial” he then continued in reference to those who deny climate change. This statement was met by large applause by those who filled Ira Allen Chapel, hitting home for a crowd that will likely be talking a lot about carbon pricing in the upcoming legislative session. Political instability, floods and mudslides, wildfires, drought, storm damage, dying coral, infrastructure loss, species extinction, melting glaciers, famine water security, ecosystem loss, our way of life, infectious disease, and sea level rise all represent the cost of carbon we are already paying Gore noted on a slide with an animated cash register racking up the cost, concluding “there is a financial risk to using fossil fuels”
It’s worth noting, that this notion does not make Gore an outlier anymore. Just last week the Governor of the bank of England, Mark Carney echoed the same message when he spoke on the increase of major weather events and the related financial cost at meeting of leading insurers at Lloyd’s of London. Additionally, going back to last year, the department of defense listed climate change as an agitating factor in areas already experiencing political instability.
As was said earlier, if Gore had sent everyone home after the “The Climate Crisis” part of his lecture, without the “Case for Hope” portion, everyone there would have a pretty doomy and gloomy demeanor for weeks to come. Instead, the mood took a 360 change with Gore trumpeting the triumphs of the past year that have put humanity on a course towards beating climate change. Among these he gave Burlington credit for achieving 100% renewable energy. He went on the new power generated in 2014 three quarters of it was renewable energy, and reflecting on the fact that those who still deny climate change can agree, renewables just make economic sense.
To close, Gore instructed the audience, “always remember, that political will is a renewable resource.” As Vermont and the rest of the nation watch national and local campaigns for political office start up in which politicians’ attention, or potential lack of attention, can greatly shape our climates future, let’s hope that holds true. Leaving Ira Allen Chapel, one couldn’t help but feel a sense of optimism, and optimism is definitely a renewable resource.
The full seminar “The Climate Crisis and the Case for Hope” can be heard courtesy of the Gund Institute for Ecological Economics
14 Sep 2015
Vermont Farmer Helps Others Produce Biofuel
 The Vermont Bioenergy Initiative, a program of the Vermont Sustainable Jobs Fund, aims to foster the sustainable bioenergy through a local production for local use model, proven to work for Vermont. Since 2003 the program has allowed Vermont farms to ease their resilience on inconsistently priced, foreign fossil fuels and other agricultural inputs. This is accomplished by focusing on biodiesel production and distribution for heating and transportation, oil crops for on-farm biodiesel and feed, grass energy for heating, and algae production for biofuels and waste management.
The Vermont Bioenergy Initiative, a program of the Vermont Sustainable Jobs Fund, aims to foster the sustainable bioenergy through a local production for local use model, proven to work for Vermont. Since 2003 the program has allowed Vermont farms to ease their resilience on inconsistently priced, foreign fossil fuels and other agricultural inputs. This is accomplished by focusing on biodiesel production and distribution for heating and transportation, oil crops for on-farm biodiesel and feed, grass energy for heating, and algae production for biofuels and waste management.
Vermont Bioenergy Initiative grantees have shown just how much the addition of biomass feedstock can contribute to sustainable agriculture. As one of these grantees, John Williamson of Stateline Farm would put it, “100 years ago everyone produced their own fuel; we are just doing that now in a different way.” This is really a novel way to look of what he is doing on his North Bennington farm. John was featured in a recent story in Daily Yonder which outlined his work and how he has begun helping his Vermont neighbors find their path to this form of sustainable, renewable energy.
For more about John Williamson’s on-farm biodiesel production, watch this video of John in self-designed Biobarn. He and Chris Callahan of University of Vermont Extension show us how they can grow oil crops, make biodiesel, feed animals, and save money!
Also, explore the initiative’s extensive and accessible set of bioenergy resources for replication in rural communities across the United States and beyond.
The Vermont Bioenergy Initiative connects diversified agriculture and local renewable energy production for on-farm and community use by supporting research, technical assistance, and infrastructure development in emerging areas of bioenergy including biodiesel production and distribution for heating and transportation, oil crops for on-farm biodiesel and feed, grass for heating, and algae production for biofuels and wastewater management. Explore the initiative’s extensive and accessible set of bioenergy resources for replication in rural communities across the United States and beyond.
Video
A series of informative educational showcase a range of biofuel possibilities; from research and crop farming to feedstocks and fuel. The videos were developed by the Vermont Sustainable Jobs Fund, UVM Extension researchers, KSE Partners, and the Vermont Bioenergy Initiative grantees.
Calculators
Two calculators, developed by UVM Extension, help connect potential costs and profits associated with oilseed production:
- Grass Biomass Production and Harvest Cost Estimator
- Vermont Oilseed Crop Production Cost and Profit Calculator
Course Work
- Biomass to Biofuels, University of Vermont: This semester-long course covers liquid and solid biofuels, biogas and bio-electricity, and environmental, social and economic issue related to biofuels. The course includes guest lecturers and field days. Available for variable credits.
- Biomass to Biofuels, Vermont Technical College: The development of this course and associated materials led to an online repository of resources for the classroom covering biomass to biofuels.
- Digester Operations Master Certificate, Vermont Technical College: a twelve week program designed for participants to work directly with operations staff of Vermont Tech’s anaerobic digester and come away with understanding of the mechanics and operations of a digester system, as well as other areas such as permitting, regulatory compliance and record keeping.
- Alternative Fuel Vehicles: Biodiesel, part of the Green Trainings series at Vermont Technical College: This 2-day course covers engine systems, biodiesel blends and biodiesel production, including a demonstration of fuel-making equipment.
- Biofuels Course at Yestermorrow Design/Build School, part of the Green Trainings series at Vermont Technical College: This weekend workshop enables students to begin replacing fossil fuels with biofuels, such as adapting engines to run on straight vegetable oil. 1 credit.
Textbook
Bioenergy: Biomass to Biofuels; is an innovative new textbook that provides insight into the potential and current advances and benefits of biofuel. Contributions include an extensive list of well-respected university extension programs, such as The University of Vermont Research Extension, as well as numerous national organizations including the US Department of Energy’s National Renewable Energy Laboratories.
Reports
A variety of reports are available which cover a range of topics including seed preparation and storage:
- Institute for Energy and the Environment at Vermont Law School.Legal & Regulatory Review of On-farm Biodiesel Production. 2015.
- Chris Callahan and Netaka White,Vermont On-Farm Oilseed Enterprises: Production Capacity and Break-even Economics. July 2013.
- Nell Campbell, Local Production for Local Use to Supply a Portion of Vermont’s Energy Needs.May 2009.
- Emily J. Stebbins. Technical and Economic Feasibility of Biodiesel Production in Vermont: Evidence From a Farm-Scale Study and a Commercial-Scale Simulation Analysis. May 2009.
- Christopher W. Callahan,A Feasibility Analysis of a Mobile Unit for Processing Oilseed Crops and Producing Biodiesel in Vermont. December 2008.
- Emily Stebbins, The Market Potential of Farm-Scale Oilseed Crop Products in Vermont. February 2008. (See also the Executive Summary)
- John Williamson & Tanner Williamson – State Line Biofuels, LLP, Chris Callahan – Callahan Engineering, PLLC, Feasibility Analysis:_Solar Seed Dryer and Storage Bin at State Line Farm, Bennington, VT. October 2008
- Christopher W. Callahan, A Feasibility Study of a Mobile Unit for Processing Oilseed Crops and Producing Biodiesel in Vermont. December 2008
- Kenneth Mulder, Ph.D., Galen Wilkerson, Emily J. Stebbins.Homegrown Fuel: Economic Feasibility of Commercial-Scale Biodiesel Production in Vermont. September 2007.
- The Vermont Biodiesel Project: Building Demand in the Biofuels Sector – Final Report. October 2006. (See also theExecutive Summary)
- Vermont Department of Buildings and General Services, Vermont Biodiesel Pilot Project: Emissions Testing of Biodiesel Blends With #6 Fuel Oil At the Waterbury State Office Complex – Final Report. September 2006.
- Laboratory and Field Testing of Biodiesel in Residential Space Heating Equipment – Final Report. August 2006.
- Vermont Biodiesel Supply Chain Survey – Final Report. April 2006.
- Wilson Engineering,Grass Energy in Vermont and the Northeast, May 2014.
Technical Advice
Connect directly with the Vermont Bioenergy Initiative’s technical assistance providers:
Oilseeds for Biofuel
- Heather Darby, Agronomic and Soils Specialist
- University of Vermont Extension, Northwest Crops and Soils Team
- (802) 524-6501
- darby@uvm.edu
- Chris Callahan, PE, Agricultural Engineer
- University of Vermont Extension
- (802) 773-3349
- callahan@uvm.edu
Grass for Heating Fuel
- Sidney Bosworth, Extension Professor
- University of Vermont College of Agriculture and Life Sciences
- (802) 656-0478
- bosworth@uvm.edu
Algae for Biodiesel
- Anju Dahiya, Instructor and Principal
- University of Vermont and GSR Solutions
- (802) 310-1936
- adahiya@uvm.edu
In early 2014 Full Sun Company, a small start-up business was co-founded by Netaka White and Davis McManus. Fueled by an interest to help family farms grow, Full Sun began processing sunflower and non-GMO canola oil crops into specialty food-grade oil and high-protein meal for the farmers. Sunflower and canola oil distribution picked up quickly through local CSAs, farm stores, specialty food shops, health and wellness centers, and direct sales to chefs in the Northeast.
Netaka White previously served as the Vermont Bioenergy Initiative’s (VBI) program director, which directly helped to develop the business model to nurture farm partnerships, both as growers and recipients of oilseed meal – the other product that’s generated from making the oil. At Full Sun oilseeds are pressed with large mechanical machinery, producing oil and a granular meal. The team at Full Sun Company learned a lot about seed storage and oil pressing from the early VBI grantees, such as John Williamson of State Line Farm, and Roger Rainville of Borderview Farm.
The first of the two products, the seed meal, has been used as fuel for pellet stoves, or as is the case with Full Sun, sold as fertilizer for crops, or nutritional meal for livestock. At full operation, Full Sun can pump out one ton of meal per day – necessary to meet the growing demand of such customers as The Intervale in Burlington, Vermont and several local pig, poultry, dairy, and beef producers.

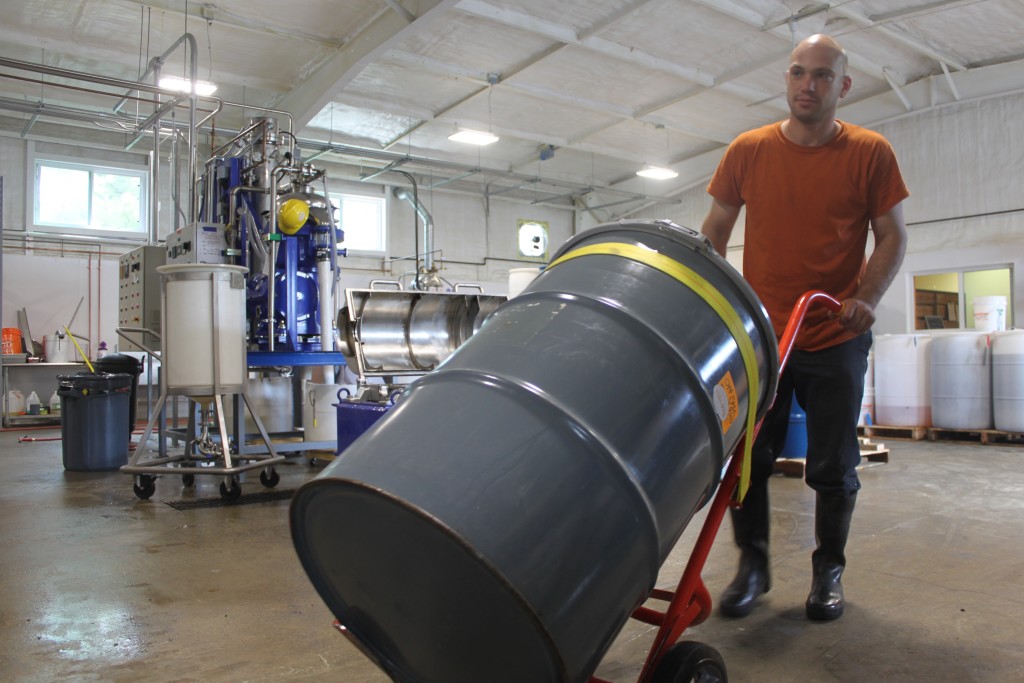
Full Sun Company employee, Zach Hartlyn, moves an off-spec oil barrel for biodiesel production
Credit: Full Sun Company
The second product, the oil, is used as culinary oil for cooking. Staying true to their commitment to an extraordinary culinary product, Full Sun Company diverts any of the oil that does not meet their standards to Vermont Bioenergy Initiative biofuel producers to undergo further processing and become biofuel. Approximately 250-300 gallons of off-spec oil for biodiesel has been processed since February, 2014.
In October, 2014, Full Sun Company halted operation to make room for growth to meet the increased demand for their products and scale up to align with Vermont’s accelerating agricultural economy. White and McManus acquired the former Vermont Soap building in Middlebury, Vermont in order to build a full scale mill and achieve their anticipated greater capacity. Over the course of one of the coldest winters in recent history, the Full Sun team made the renovations and adjustments needed to repurpose the building into the first non-GMO verified oil mill in New England. By March of 2015 Full Sun Company had pressed sunflower and canola seeds to make their first batch of specialty oils. The new operation can yield 130 gallons of oil per day – about 2600 gallons per month!
With no shortage of innovation or ambition, White notes, “David and I are in this with the interest of having a transformative effect on local agriculture and food systems.” Well on their way, the operation is certified GMO free, and the next steps are being taken towards becoming certified organic.
As they grow, Full Sun would like to buy from local grower-suppliers and work with local businesses to package and label feed to be distributed to farmers of varying sizes, from backyard chicken growers to larger operations. Collaborating with Vermont breweries and distilleries is also in queue. Full Sun is working with one local distillery to put together “a package” for farmers so they have markets for profitable grain crops throughout four years of rotation (rye, wheat, sunflowers, etc.) and can offer farmers the indexed prices for these locally grown grains and oilseeds.
13 Jul 2015
Making Biofuel
 Making biofuel, it sounds like a complicated process taking place in a laboratory somewhere, but in reality it’s quite simple and happening in small, rural Vermont farms. Vermont farmers like John Williamson of State Line Farm and others are electing to create their own fuel and meal. These farmers are enjoying the benefits of the distance to source resiliency and cost reliability that comes with the local production for local use biofuel model they have adopted.
Making biofuel, it sounds like a complicated process taking place in a laboratory somewhere, but in reality it’s quite simple and happening in small, rural Vermont farms. Vermont farmers like John Williamson of State Line Farm and others are electing to create their own fuel and meal. These farmers are enjoying the benefits of the distance to source resiliency and cost reliability that comes with the local production for local use biofuel model they have adopted.
As John Williamson, a Vermont Bioenergy grant recipient says, “100 years ago everyone produced their own fuel; we are just doing that now in a different way.” This is a novel way to look at what he is doing on his North Bennington farm. Vermont farmers in the past would plan to allocate their acreage to feed their livestock, some of which aided in energy-intensive farm activities like plowing, planting, and the eventual harvesting of their field. With the local production for local use model, John is now thinking about how to feed his tractor so he can do the same activities. So what is the feed of choice for John’s John Deer tractor? Sunflowers!
John loads dry and clean sunflower seeds into hoppers on a TabyPressen Oilpress, where screw augers push the seed through a narrow dye. Extracted oil oozes from the side of the barrel and is collected in settling tanks while pelletized meal is pushed through the dye at the front and is stored in one-ton agricultural sacks. The first of the two byproducts, the seed meal, can fuel pellet stoves, serve as fertilizer for crops, or find its way to local Vermont farms to supplement animal nutrition as livestock feed. The second byproduct, the fuel, could at this point be used as culinary oil for cooking, but instead will experience further refinement and become biofuel.
The processing of the oil takes place in Johns self-designed Biobarn. In the below video, John Williamson and Chris Callahan of University of Vermont Extension show us how they can grow oil crops, make biodiesel, feed animals, and save money!
01 Jun 2015
Food Versus Fuel – Local Production for Local Use – Biodiesel as Part of Sustainable Agriculture
Nationally, corn-based ethanol and palm oil based biodiesel are gaining negative attention for their impacts on the environment and food security. But here in Vermont, farms are producing on-farm biodiesel to power equipment and operations on the farm and the local farm community. This is a profoundly different model from national and international biofuel production. Agricultural Engineering and Agronomy Researchers at University of Vermont Extension in partnership with farmers and the Vermont Bioenergy Initiative have developed a model of local minded, on-farm production of biofuels that can help rural communities transition away from unsustainable models of food, feed and fuel production.
National and global models of corn-ethanol and soy oil-biodiesel production are resulting in large-scale land conversions in some parts of the world, in particular to a loss of native grass and forestland. This type of biofuel production is not happening in Vermont, where bioenergy production incorporates rotational oilseed crops like sunflowers and soybeans on Vermont farms.
Locally produced biodiesel supports resiliency in Vermont, a cold climate state which is particularly dependent on oil. Over $1 billion leaves the state for heating and transportation fuel costs. Heating and fuel independence by producing on-farm biodiesel provides farmers fuel security which is comparable to that which is sought by Vermont’s local food movement.
The local production for local use model results in two products from one crop: oil and meal (animal feed or fertilizer). By growing oilseed and pressing the seed to extract the oil, farms are creating a valuable livestock feed at home, rather than importing it. The oil can be sold as a food product, used directly in a converted engine or converted to biodiesel for use in a standard diesel engine. In this way, oilseed crops offer flexibility in the end-use of the products. US corn-based ethanol mandates are raising grain costs nationally, making feed expensive for Vermont farmers. Local bioenergy production means farmers produce their own feed, fuel, and fertilizer for on-farm use, at a fraction of the cost and more stable prices. Reduced and stable prices for feed, fuel, and fertilizer can mean improved economic viability for Vermont farms and more stable food prices for Vermont consumers in the future.
Overall viability can be seen in the local production for local use model by considering economics, energy and carbon emissions. Biodiesel production costs of between $0.60 and $2.52 per gallon have been estimated for farm-scale production models, which are generally below market price for diesel fuel. The net energy return in Vermont on-farm biodiesel operations has been estimated at between 2.6 and 5.9 times the invested energy (i.e. more energy out than was required to produce the fuel), demonstrating strong returns and potential for improvement with increased scale. Furthermore, oilseed-based production of biodiesel has been estimated to result in a net reduction of carbon dioxide emissions of up to 1420 lbs. per acre, the equivalent of about 1500 miles of car travel per year.
Categorizing the Vermont biofuel model with national models and trends is inaccurate, considering the innovative and efficient systems benefiting Vermont farmers. While national and international analysis weighs the benefits of food versus fuel, the model is quite unique in Vermont and the food versus fuel challenge is well met. The model developed in Vermont does however have wider-reaching implications in that this can be replicated in rural farm communities across the US.
As John Williamson of Stateline Farm, a Vermont Bioenergy grant recipient says, “100 years ago everyone produced their own fuel; we are just doing that now in a different way.”
In order to meet the goals set by Vermont’s comprehensive energy plan for Vermont to produce 90 percent of the state’s energy needs from renewables by 2050 and reduce Vermont’s greenhouse gas emissions by 50 percent from a 1990 baseline, Vermont farmers will have an important role to play. As Vermont experiences growth in food-related businesses and jobs, decisions about energy become more important prompting statewide energy and agriculture collaborations. In the following episodes of Across the Fence, UVM Extension agricultural engineer and Vermont Bioenergy Initiative biofuels consultant, Chris Callahan, shares two stories about Vermont farmers who are rethinking their on-farm energy. In both examples UVM extension is able to work with the farmers to help make cleaner, renewable on-farm energy sources a practical solution that saves money and results in greenhouse gas reductions.
Learn more in a series of on-farm energy case studies produced by Vermont’s Farm to Plate Initiative.
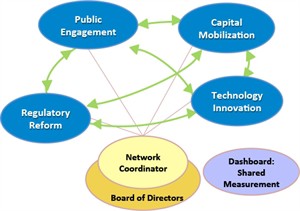
The EAN’s 4 Key Leverage Points of capital mobilization, public engagement, technology innovation, and regulatory reform
The Energy Action Network (EAN) is a community of a community of Green Mountain State stakeholders working to change the Vermont energy landscape “to end Vermont’s reliance on fossil fuels and to create clean, affordable energy and secure electric, heating, and transportation systems for the 21st century.” Their goals are consistent with the State of Vermont 2011 Comprehensive Energy Plan, which aims to meet 90% of Vermont’s energy needs through efficiency and renewable sources by 2050.
EAN has identified a series of pathways for Vermont for Vermont to accomplish the paradigm shift of 90% renewables by 2050. Membership is structured into working groups focused on four “leverage points” capital mobilization, public engagement, technology innovation, and regulatory reform. Current projects include alterations to Act 250, changes in zoning laws, programs to promote bringing rental properties into efficiency standards, and assessing current land use for its potential for bioenergy and solar projects.
One notable awareness vehicle, Brighter Vermont, encourages Vermonters to change the way common energy use and think more about where energy comes from. Read more about how Brighter Vermont helps change energy behavior. EAN also works with municipalities and recently helped Montpelier plan for a 15 year track to become the first state capital to accomplish all of its energy needs with renewable energy. On February 12, 2015 the Montpelier City council accepted and endorsed the plan to make Montpelier a “net zero” city.
Currently, EAN is working with the Vermont Sustainable Jobs Fund to expand the Vermont Energy Atlas website into the Community Energy Dashboard. The Dashboard will enable communities to understand their energy use and make clean energy choices and investments across all energy sectors—heating, transportation, and electricity. The Dashboard will make energy use visible and understandable to consumers and communities by showing town-level progress toward Vermont’s 90% renewables by 2050 goal. The Dashboard will also shows existing and potential renewable energy sites (solar, wind, hydro, biomass). We will provide updates as they develop. Stay tuned into the Vermont Bioenergy Field Notes blog and visit the Energy Action Network website to learn more.


















